From Points to Insights: How AI Is Transforming Map Interfaces

In his magnum opus, “Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics,” Alfred Korzybski famously stated that the map is not the territory. Our UI/UX designer, Sergey Gladkiy, explains how we can utilize AI to enhance these useful representations of reality and enrich our understanding of the world.
UIs with interactive maps have long become a usual deal in tons of digital products—from taxi and shopping apps to logistics and citywide monitoring platforms. But most of the time, such maps only display “what’s where” without helping users understand why it matters or what to do next.
Each dot on a map represents a single data point. But when there are hundreds or thousands of them, maps become cluttered and lose their analytical power. Users are then left deciphering static visuals with little guidance, wasting time and misinterpreting things.
AI can help battle this trend—we must make our maps think. And AI can be used to turn senseless, context-lacking maps into dynamic, context-aware tools that actually help users decide their next step instead of guessing.
Doing it Wrong: Dots Without Insights
Most of today’s dashboards usually feature maps that simply show locations—be it traditional geolocations or incidents, clients, or fleet movements. However, not many maps bother personalizing the experience and interpreting what actions with the geopoints are available for users.
As such, all we get is a confusing display of disconnected fragments, which restricts users’ actions—they simply stop and stare at the map. It’s a matter of cause and effect—it comes down to a range of consequences that affect the overall UX, such as:
- Lack of immediate context forces users to overthink and seek functionality patterns manually;
- Maps are used as static visuals rather than dynamic analytic tools;
- More time is spent by users pondering what data means than what to do next.
To mitigate the above, we need something that would enable our maps to deliver clear, concise, and contextual answers to user geo-queries. Not just approximate areas and visuals to impress. AI happens to do a great job at calibrating today’s interactive maps.
The Solution: AI + Geodata = Smart Maps
By assigning a fitting AI model to sift through, collect, and analyze some rich geodata, we can achieve an ultimately context-driven and, thus, better-personalized foundation for map dashboards. And even beyond that, AI unlocks an entirely new field of utilities a smart map can feature.
How does AI redefine interactive maps, and which utilities does it entail? There are a couple of standout applications.
Clustering and summaries
In most integrated maps, hundreds or even thousands of markers clutter the display, confusing and overwhelming users. This is where AI-powered clustering can help—it automatically groups nearby or related points so that the user gets a simplified visual field, with only the action patterns that matter narrowed down.
AI techniques like k-means, DBSCAN or OPTICS and HDBSCAN, among others, group data based on proximity, density, similarity, or type of event. The principle is this: you take a noise-filled scatter of points and turn it into coherent clusters, each representing a meaningful data summary.
This is a great approach that helps make things that much easier for human perception of map interfaces because it grants
- Visual simplicity: Instead of sifting through clutter, users see well-defined clusters with aggregated stats.
- Quick pattern spotting: Hotspots, trends, and outliers stand out naturally to the human eye—no manual analysis is needed.
- Performance: Maps load faster because fewer elements are rendered, smoothing out the UX (especially when running on live data).
As a result of implementing intelligent clustering, you get less noise and more action. Data overload becomes manageable. Hidden insights surface more easily. Users spend much less time interpreting stuff and more time reaching their goals.
Forecasting and scenario modeling
AI-powered maps can also be leveraged as anticipatory engines that help predict future outcomes and let users simulate scenarios before committing resources. For example, users can use smart maps to predict gridlock in specific zones during rush hour or forecast delivery demand based on weather and historical trends.
AI systems such as Aimsun Live and PTV Vissim integrate live data from vehicle sensors, cameras, and crowdsourced traffic feeds with machine learning models (including graph neural networks) to forecast congestion 30–60 minutes ahead. These systems are already helping traffic control operators to sensitively adjust road signals and dispatch quick-response teams.
On the flip side, big logistics firms, including Amazon, have grown to rely quite a bit on live predictive analytics that combine weather, historical order data, and real-time traffic. Tons of AI-enabled data analysis occurs to forecast delivery needs and optimize routes dynamically.
For some examples:
- A U.S. e-commerce case study showed that AI-driven routing cut delivery times by ~20% and fuel use by ~15%.
- Amazon’s upcoming AI-enabled maps and even delivery glasses will help drivers navigate even hands-free in complex environments.
By projecting various nearest outcomes — like traffic buildup, delivery volume spikes, or energy usage — AI tools help users model diverse scenarios, which they can test before implementing any real-world changes.
But prediction doesn’t stop at logistics or city streets. AI also enables global-scale environmental monitoring, providing high-resolution insights into land use, ecological change, and the human footprint.
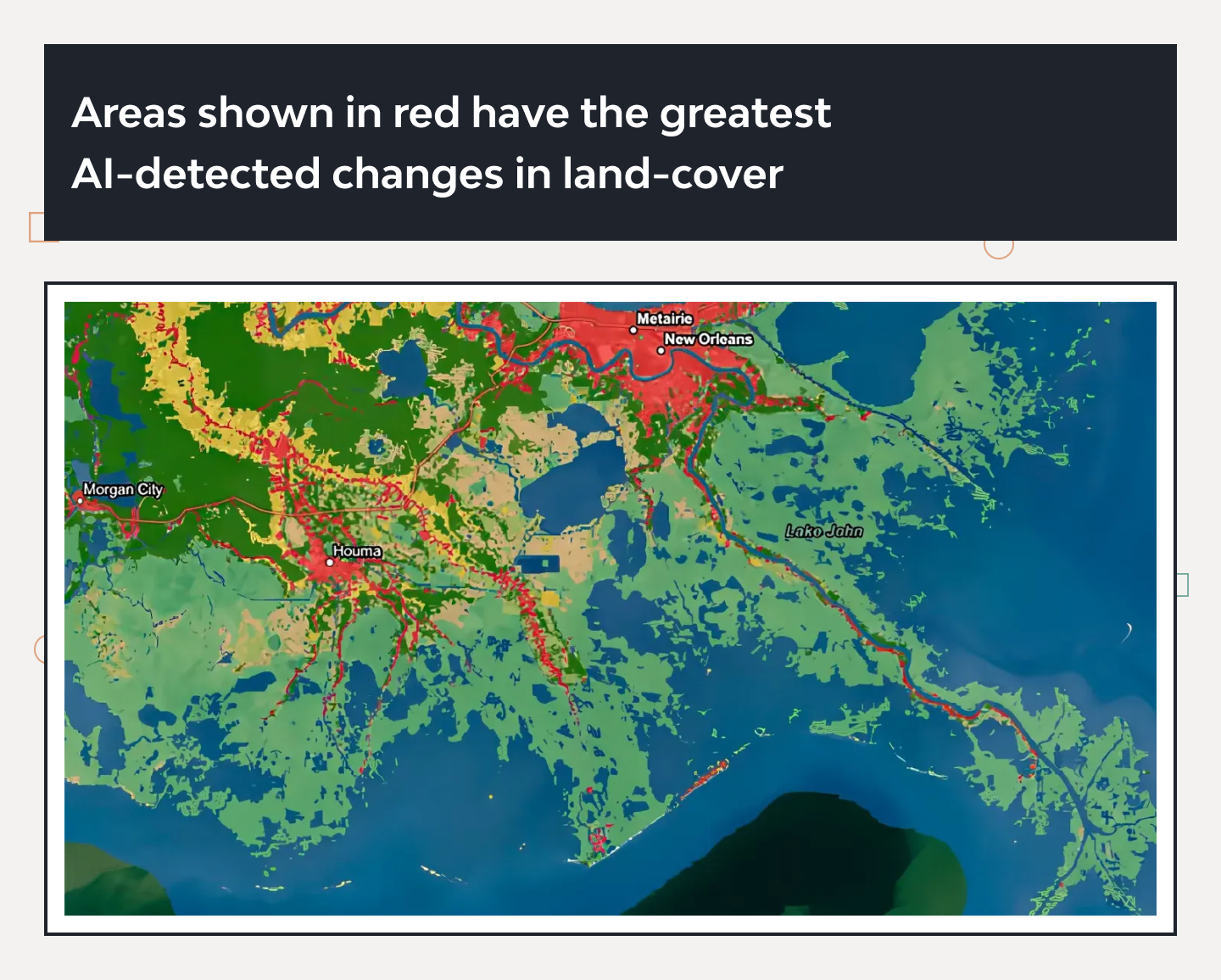
📸 Monitoring Changes Automatically and at Scale
A compelling example is Microsoft’s partnership with Esri and Impact Observatory. Their AI-powered global land cover map monitors environmental change at an ultra-fine 10-meter resolution—a leap forward from conventional tracking.
This geospatial AI model allows researchers and planners to answer big-picture questions about climate impact, deforestation, and urban expansion—automatically and continuously.
A huge range of custom scenarios can be emulated if you throw your AI model some elaborate what-ifs, like:
- “What if a factory shift starts at 6 AM?” (AI can predict road congestion and delivery delays to keep in time).
- “What if a storm drops rain from 1 PM–3 PM?” (AI will anticipate increased delivery times and adjust staffing).
- “What if we close a road for repair?” (AI will help evaluate alternate routes and response times).
Trained on such what-if datasets, the AI integrated, say, with a food delivery app will track routes precisely and insightfully, allowing the client to track delivery movements and time transparently, with even potential difficulties accounted for.
Adaptive user experience
On top of simply showing data, AI-powered maps can adjust in real-time to match each user’s role, context, and behavior, making sure everyone sees exactly what they need, when they need it. This is achieved through role-based customization, where the map’s integrated AI learns to recognize user personas and personalizes the user experience accordingly.
AI systems learn from how users interact with the map and leverage behavioral data to layer to individualize the UX. As a result:
- Analysts get deep-dive layers, allowing interrogation of raw data, filters, and underlying correlations.
- For strategic decision-making, managers can view high-level summaries like cluster trends, risk zones, or performance indicators.
- Operators see alert-driven interfaces showing only urgent, immediate events for real-time response.
The user interactions and behaviors that AI learns from include zooming into city blocks, toggling map layers, or dismissing notifications. Over time, the map learns to prioritize the most frequently accessed features, simplify less-used elements, and anticipate following user actions to reduce clicks and navigation fatigue.
More than that, building on adaptive UI science, maps can even adjust based on:
- User context — location, type of device used, or even cognitive load and mood;
- Interaction flow — AI can subtly guide users to likely next steps;
- Environmental signals — like critical alerts or shifting priorities.
This may be a simple play of words, but all of the smart functionality allows us to create interactive maps that aren’t just user-friendly but user-smart.
Interpreting anomalies
Last but certainly not least, AI has the capacity to turn maps from simple alert tools to intelligent systems capable of understanding and explaining anomalies. For users who need more than indications and signals (usually, analysts, managers, and other decision-making specialists), a smart map can provide clarity and underlying factors to each geopoint, object, or anomaly.
All thanks to AI’s inherent ability to efficiently detect hidden irregularities. Today’s contextual anomaly detection systems can analyze patterns based on time, location, and domain context. They can then flag data points that deviate from the norm unexpectedly — such as an unusual surge of activity in a quiet neighborhood.
In urban settings, AI can monitor flow patterns or vehicle paths to quickly detect route deviations or sudden stoppages that humans might miss among thousands of data points.
And the best thing is that AI goes beyond alerts, becoming able actually to explain causes of events. For instance:
- Explainable AI (XAI) techniques, like SHAP, LIME, or saliency maps, provide context why a location was flagged. Was it due to density, unusual timing, or deviation from historic norms?
- Smart visual overlays on the map can highlight contributing factors to the anomaly, showing whether it originates from a clustering shift, an unusual trend spike, or a pattern break.
Furthermore, by wielding historical context, AI helps minimize false alarms. It compares anomalies to past data snapshots and detects barometric shifts, like weather-related disruptions vs. genuine security or logistics issues.
For example, Wuhan’s Traffic‑ConvLSTM flagged crowded areas during holidays more accurately by learning from historical patterns and thus avoiding many unnecessary alerts.
Another example is ArcGIS, developed by Esri—the geographic approach to real-world problem-solving through powerful AI integrations. From forecasting to anomaly detection, it delivers dynamic, role-aware, and context-rich insights across industries—all visualized through spatial intelligence.
Whether it’s optimizing emergency responses, planning urban development, or managing infrastructure, ArcGIS uses AI to anticipate, adapt, and automate.
With an overall individualized, contextualized approach, AI also does a great job at communicating issues and anomalies because:
- Alerts are accompanied by clear explanations that stimulate user trust and help handle panic.
- Users get contextualized visuals, not cryptic signals for savvy users, which makes them respond faster and more precisely.
- By logging anomaly triggers and explanations, AI systems improve continually, growing more accurate and trustworthy from interaction to interaction.
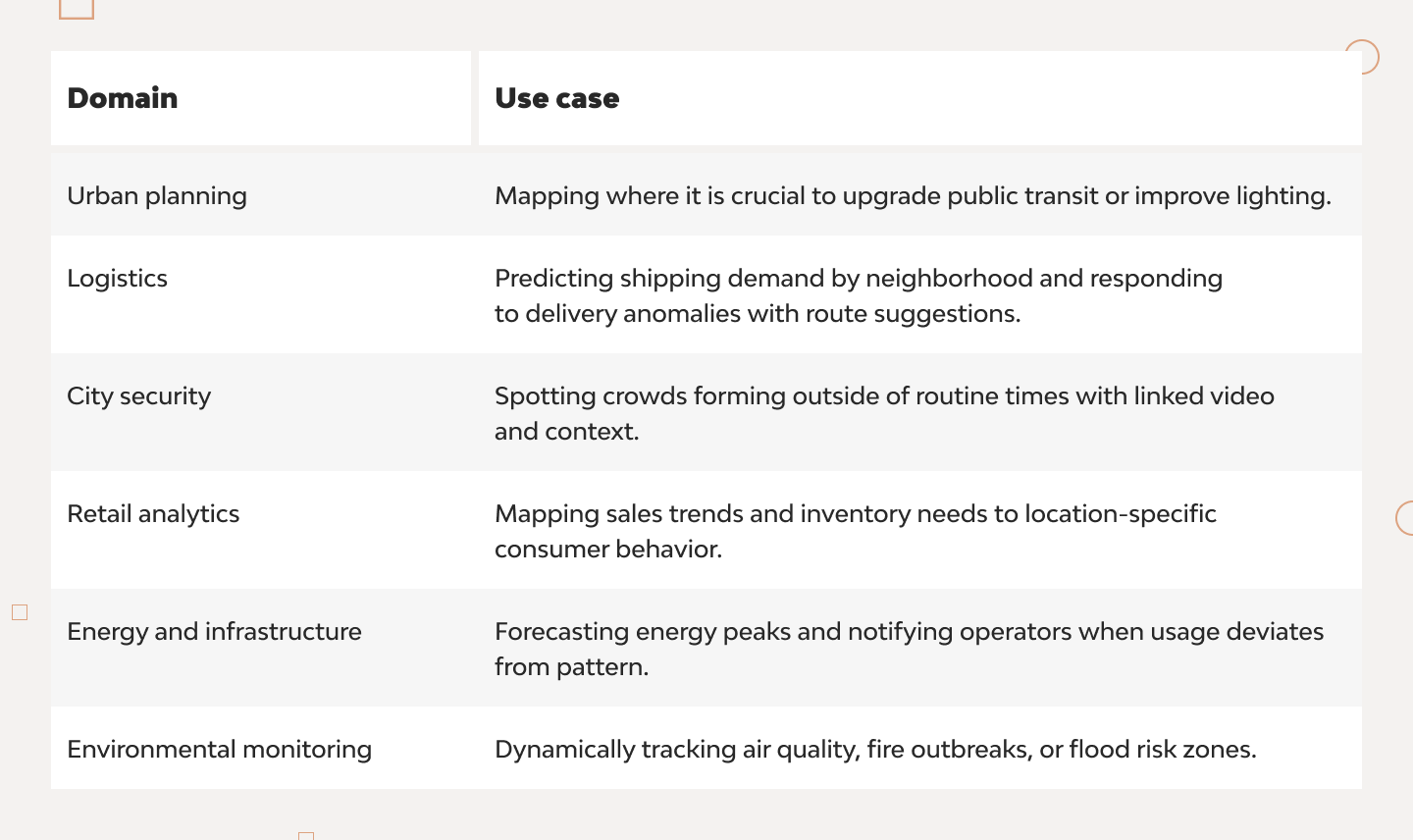
More Real-World Applications
More use cases for AI-equipped, feature-rich, and contextualized smart maps are limited only by practical need, imagination, or resources. As AI becomes better at fusing insights on the map with real-time data, we get more space to cover with new innovative map implementations for all relevant industries.
Why Smart Maps Matter Now
It’s incredible what a data-dense yet time-scarce world we live in. Today, people either choose the shortest, quickest access to condensed, relevant information or don’t bother inspecting it at all (most of the time). So basic point maps just don’t cut it anymore.
AI turns things around and successfully reinvents the wheel here by allowing us to generate insights from spatial, temporal, and behavioral patterns and even project them into what lies ahead. All on the continuously customizable, self-learning map.
We get all the tech capacities we need to implement predictive, action-ready maps that are more than simply interactive. Such maps are perfect for fast-moving crises, urban growth, or climate adaptation. And adopting them from the get-go allows you to be well-prepared for users’ individual demands.
Final Thoughts
AI comes in to connect the dots on the map for us, so that users are not bothered by even a slight extra action or manual effort. In this day and age, nothing can be worse than confusing or bothering a target user or client, prolonging unnecessary interactions, and piling up a mental strain on people.
With thorough implementation, intelligent systems that are integrated with maps and fed proper geodata can also help:
- Reveal spatial patterns and connections
- Anticipate outcomes and emulate scenarios
- Dig out tailored, role-based insights
- Explain deviations with historical context
Making your interactive map smarter and more actionable should enable you to ultimately accelerate that map’s UX, i.e., how fast users move from screen to screen, make decisions, and reach goals. This is equally beneficial for city planners, logistics teams, monitors, or retailers.
If you have questions regarding this article’s topics or would like to get some extra consulting, make sure to direct them to yours truly. See you around!