UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide]
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide]](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/UX-Audit-Service-How-to-Perform-and-Get-Visible-Results-Cover.jpg)
This article is focused on user experience audit. It examines the reasons for performing a UX audit, its main stages, outputs, and the service cost. Do you want to know what this method is and what its benefits are? Then, you are on the right page.
Performing a user experience audit may be required at various stages of product development. At the initial stages (discovery or pre-development), it can help define users’ needs and expectations and thus reduce the cost of fixing errors later. For a product that has already been on the market for some time, it helps identify obstacles to achieving user goals. And after significant changes in the product or its functionality, a UX audit allows for evaluating their impact on the UX and identifying possible shortcomings.
In each case, while the company has to allocate certain resources to perform a UX audit, the costs are usually recouped in numerous ways. The benefits may include reducing frustrated customers, increasing sales, speeding up development while decreasing the chances of mistakes, strengthening brand reputation, and enhancing employee motivation.
Working at Django Stars with projects in fintech, travel, and e-commerce, I know firsthand how high design requirements are. When it comes to creating the interface of an app that makes users’ life easier, it’s often about how to organize large amounts of information in a light and attractive way for the user. In this article, I turn to my experience performing a UX audit for PADI Travel, a global booking platform with the widest selection of liveaboards, dive resorts, and dive centers worldwide. A UX audit that this case involved covers a wider range of services than our usual UX review.
Usability audit draws product development to the next level. That’s why it makes sense to figure out how it works.
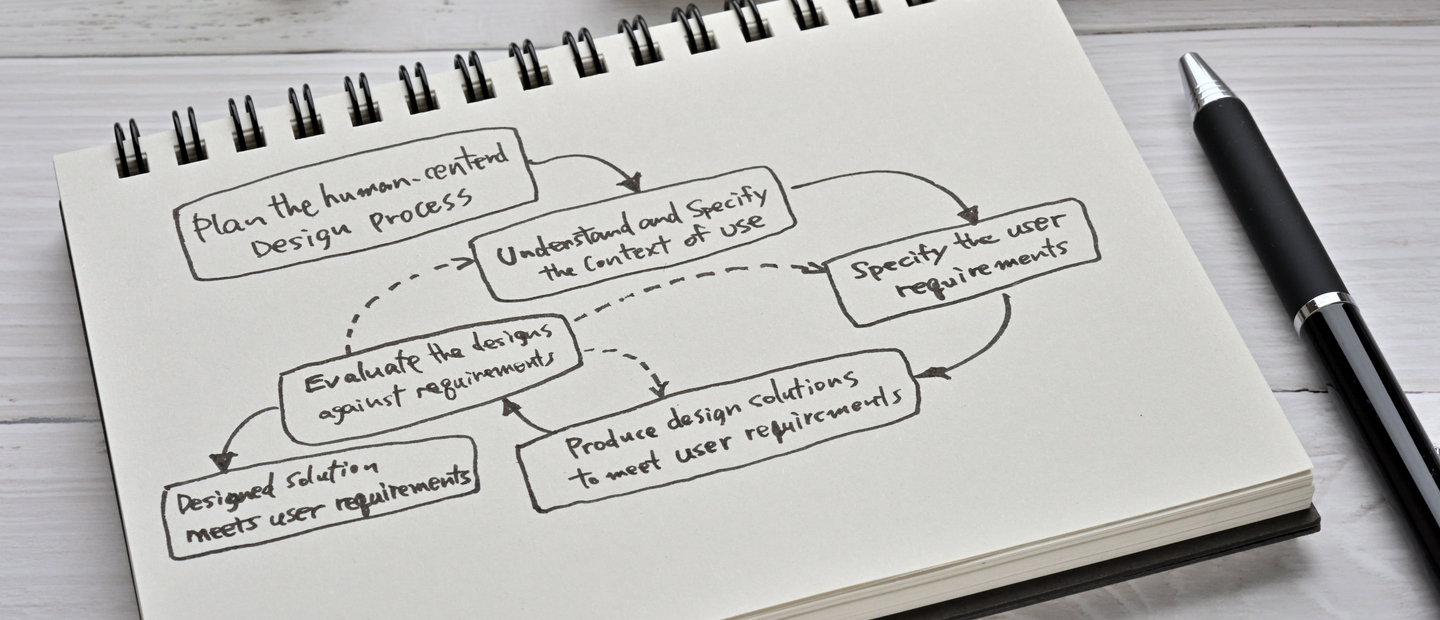
What is a UX audit?
A UX audit (sometimes called a UX review service) is the professional evaluation of the product’s usability to see if it meets business, user experience, and accessibility requirements.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 1](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/UX-audit.png)
UX audit allows designers to identify problems users encounter when interacting with the interface and to assess business using actual data.
During a UX audit, UX auditors measure, test, and analyze:
- broken links
- inconsistencies with the design system (fonts, colors, patterns, etc.)
- layout and hierarchy inconsistencies
- outdated content
- problematic spots in the user’s path
- convenience and accessibility in use
- usability heuristics
- product branding
- product design according to business and user interaction goals
- analytics of traffic, engagement, conversion rates, etc.
- navigation and search
- page load speed and key performance metrics
At the end of the UX design audit, the UX auditor creates a report with actionable recommendations for solving any problems in the interface or optimizing the product.
For example, here’s how audit recommendations for a traveltech app may look like:
- It’s necessary to change the order of the sections in the menu depending on the number of clicks from the analytics.
- Change the photo carousel to a wizard (a step-by-step interface), where the user can select the desired section directly. The space occupied by the carousel can be used more efficiently.
- Add the option to download a ticket to a mobile device for ease of use while traveling.
- Provide better descriptions of the proposed plans with a comparison and links to relevant plan pages (open in new windows). Also, consider changing the name of the “Contact Consultant” button to “Request for Quote” and make it more visible throughout the page.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 2](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Examples-of-Audit-Recommendations-for-a-Traveltech-App.png)
What Problems Can a Product Design Audit Solve?
UX/UI audit can help find places in the product where the user encounters problems and ways to solve them, understanding how the user flow can be improved. Also, the development team can conduct user experience audits to collect and analyze data from analytics.
Performance analysis of the product (how quickly pages load, whether the user can interact with the interface quickly enough, when the first content appears, etc.) is also the part of the UX audit.
Here is an example of what a website performance score may look like in a UX report:
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 3](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Website-Performance.png)
It suggests the following conclusions:
Core Web Vitals assessment failed. The main metrics are low, it is necessary to reduce the time to the first interaction with the interface, reduce the javascript loading time and optimize the size of the loaded content. Especially on mobile devices.
In general, an app UX analysis can help with many questions that may seem simple, but only at first glance — because they require data-based answers, not assumptions:
- What exactly do the key users’ portraits look like?
- Where most often do users stop to complete tasks when interacting with the product and leave it?
- Why is some functionality not actively used by users?
- Does the content help perform the necessary tasks, and do users still have questions?
- What are the problems with the UI?
- Does the design of the pages correspond to a uniform style?
- What needs to be done to optimize the process of booking, checkout, searching on the website, etc.?
- Do users like the website? Will they return? If not, why?
- Do the interface elements help at each stage of task performance? Which of them should be changed?
When It’s Optimal to Perform a UX Audit?
One of the first questions regarding the UX audit is this: When should it be conducted?
As I mentioned above, performing usability audits can provide certain benefits at different stages of the product’s life cycle. As for the most appropriate reasons to consider this measure, a UX audit may take place when a business party wants:
- to redesign an existing product
- to improve existing metrics and understand which metrics to track
- to optimize page loading to enhance user experience and SEO (performance in search engines)
- to identify problems in the interface and understand what needs to be addressed first
- to analyze pages for style consistency (whether the styles of different pages of the website correspond to a sole style guide)
- to improve the user flow
- to implement new functionality in the product: UX audit may be used to validate the decision
- to make the product more adequate to the goals of the business
What Are the Benefits from a UX Audit
Here’s the list of the main benefits that may cause a company to conduct its app ux audit:
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 4](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Main-Benefits-of-a-UX-Audit.png)
- Increasing user loyalty. An audit can help increase user loyalty and satisfaction with the product leading to a boost in conversion rates and sales volume.
- More effective fulfillment of the product goals. Enhanced success in meeting product goals will directly affect the number of regular users and their retention.
- Improving overall user impression of the brand. Customers will appreciate the company’s concern for them, which will contribute to recognition and growth.
- Identifying the root cause of existing problems (for example, a large number of unfinished purchases, customer churn, navigation problems, etc.). It helps determine what needs to be changed first.
Main Steps of UX Audit Process
Specifying Objectives
Before performing an audit, it’s necessary to understand the product and find out who are the stakeholders and what problems need to be solved. For this, it’s required to interview interested parties familiar with the site (product owner, developers, managers, support staff, etc.). During the interview, it’s necessary to collect the following information:
- What was the site created for? What problems does it solve?
- What issues and errors exist now?
- What is to be improved?
- What has already been done, and how has it affected the metrics?
- What are the business goals? What are the indicators of their achievement?
- How much time is available for the audit? What resources are available?
All information received should provide a clear understanding of the objectives of the business and the UX audit. It’s important to ensure that the audit objectives help achieve business objectives.
Analytics and Insights
Google Analytics, can help understand better who the product users are, how metrics characterize their interaction with the website, and which pages are visited more. Also, it can show the flow of transitions on the website, the most visited pages, and indicators of user outflow, conversions, and others. The required amount of data and its collection period depends on the number of active users and the required accuracy of the results. Data for the last 3 months is usually required to be considered valid and to analyze most indicators.
To illustrate, below is a screenshot from Google Analytics 4 for a website that shows 74K visitors in total during the selected period. Most of them, 64K, are new users. It also reveals that users from the USA prevail in the last half hour.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 5](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Device-Category-Report-in-Google-Analytics.png)
Analyzing User Experience
Google Analytics helps to reveal the existing problems in the product. A UX analysis is carried out to understand them in more detail and the reasons for their occurrence. Examples of weaknesses that can be identified at this stage include suboptimal navigation, difficulties with form filling, and difficulties when going through the flow. The developers can get insights into whether the content helps the user and whether it corresponds to the functionality. Also, they can check the adaptability of the interface and the visual component, the composition of page elements, compliance with standards, and others.
Let’s look at a few real-life examples of what can be improved in UX.
1. Drop-down menus excess.
This one I took from the website of a UK-based multinational grocery and general merchandise retailer Tesco. It contains many drop-down navigation menus making it difficult for the user to analyze the available items. This means more time spent searching for what’s needed on the website and increases the time when ordering goods.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 6](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Examples-Drop-down-menus-excess.png)
2. Style cluttering.
Another common problem is the use of a large number of colors, fonts, and other styles. In combination, they reduce the perception of the content, distract from the website’s main purpose, and increase the cognitive load on the user (the mental effort required to process information). That negatively affects conversion, sales, and the overall impression of the product. Here’s an example of a school website that is difficult to perceive due to poor structure, styles, and fonts.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 7](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Examples-Style-cluttering.png)
3. Inconvenient categorization.
In the following example with a large British catalog retailer Argos, the Technology subcategory headings are not clickable. And while some subcategories like Televisions have the Shop All option, others like Tablets & iPads don’t, forcing users to use too narrow a range of products.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 8](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Examples-Inconvenient-categorization.png)
Thus, a heuristic assessment of the product’s ease of use is carried out. Taking into account the features of various devices and platforms, a UX auditor can conduct an analysis for compliance with guidelines and general usability patterns.
Tracking Technical Errors
Tracking technical errors is an important step because problems in user interaction with the product lead to a bad user experience, and increase the time for successfully completing the user flow. Performance and analytics indicators will also deteriorate.
To avoid the decline of analytics indicators, it’s necessary to focus on finding these errors during the website user experience audit and solve them later after analyzing and prioritizing the results of the UX audit. What’s important, this stage will help prioritize which technical problems should be worked on first in terms of design and benefit for users.
UX Audit Outputs
The UX audit output is the UX audit report that describes:
- the project (briefly) with the audit participants, deadlines, goals, etc. (including the methodology and tools used during the audit)
- results of the website performance analysis (using the main metrics of page loading speed and operation with an issue description and a screenshot)
- insights from Google Analytics (general info about users, their devices, sessions by devices, the most visited pages, user behavior, user flow, avg. browser-based page loading time, etc.)
- all discovered users’ pain points and places in the product where they can be solved
- UX issues and suggestions for improvement
Depending on the purpose of the audit, the report may include the Customer Journey Map, usability testing scenarios, results of the tests, etc.
It’s also possible to present the results in a different form if that aligns with the audit tasks and better reveals the obtained results.
UX Audit Services Cost
The price for conducting a UX audit depends on several factors, such as the project timeline, audit goals, number of pages, and required tools. For example:
- For the landing page, it takes approximately 2-3 days to analyze and compile all the results into a report.
- If it is a website with a large number of pages and features, its usability audit may take 4-10 days.
The cost in the above cases will be formed considering the audit duration and the hourly rates of the specialists involved.
To shorten the UX audit period, the client can outline the key functionality that has to be checked, thus reducing the time required for analysis.
Django Stars Experience
Conducting a UX audit can be resource-intensive and thus requires a clear understanding of its objectives and the results it can provide. For this reason, while the Django Stars team has extensive experience designing web app interfaces (including quite complex ones), not many cases in our portfolio involve usability audits.
An interesting case with UX audit from my practice is for a travel booking platform PADI Travel where users can choose between many packages with various options. Over years of operation, the business side reviewed its vision regarding the platform’s UI/UX. Research for where to direct further changes led to a need for a usability audit.
![UX Audit Service: How to Perform and Get Visible Results [Guide] 9](https://djangostars.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/PADI-Travel-Website.png)
Usually, when redesigning a project (except for starting from scratch when a Discovery phase is carried out), the Django Stars team includes a UX review — namely, the searching for UX errors. To proceed with a UX audit, the formed set of hypotheses (even if it’s based on rich experience) should be tested with users. Specifically, conducting a UX audit like that for PADI travel required complementing this part with goal identification, analytics, performance check, user interviews, and other available tools. Such an approach allows for a comprehensive UX assessment and the detailed identification of problems with their essential inclusion in an audit report.
Final Thoughts
A user experience audit is indispensable when it comes to identifying valuable information about the product’s performance and UX issues. With the proper approach, it helps to effectively analyze the existing functionality and prioritize directions for UX improvement. After the UX audit and analyzing its results, it becomes possible to get a clear overall picture regarding the product users, what they encounter, how to solve the discovered problems, and what exactly needs to be improved to achieve the business goals.
The UX audit process results in a list of specific, actionable recommendations that will help determine which priority parts of the product should be strengthened first and which problems should be corrected.
While a UX audit process may seem highly complicated at first glance, the defined goals, optimal conducting structure, and proper toolset make it clear and effective. Сontact Django Stars if you are looking for expert assistance with a UX audit, software development, and related matters.
- What factors influence the final UX audit cost?
- The final cost of a UX audit is formed based on the project timeline, the audit objectives, the complexity of the website or app being audited, the number of pages and user flows, and the necessary tools and resources.
- How long does it take to conduct a UX audit with Django Stars?
- For the landing page, it takes approximately 2-3 days to analyze and compile all the results into a report. If it is a website with a large number of pages and features, a usability audit may take 4-10 days. Сontact our specialists for a more accurate estimate of the UX audit duration for your project.
- How often should I repeat UX audit for my product?
- There's no set time frame for when to repeat a UX audit, as it largely depends on the specific product and its development cycle. However, it may be worthwhile to conduct regular UX audits throughout the product's lifecycle to ensure ongoing improvement and user satisfaction.