6 Examples of AI in Financial Services & Banking

Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the financial services industry, making it faster, more efficient, and more personalized than ever before. From fraud detection to chatbots to investment advice, AI is being used in a variety of ways to improve the financial services experience for both businesses and consumers.
Less than 70 years from the day when the very term Artificial Intelligence came into existence, it’s become an integral part of the most demanding and fast-paced industries. Forward-thinking executive managers and business owners actively explore new AI use in finance and other areas to get a competitive edge on the market.
More often than not, we don’t realize how much Artificial Intelligence is involved in our day-to-day life. In this article, we will explore six examples of how AI is being used in financial services today and the benefits it brings to the industry.
Benefits of AI in Finance
AI has already brought significant advancements to the financial industry and continues to do so day by day. It’s prompting financial institutions to rethink the way they operate, transforming the customer experience. Here are some key benefits of AI in fintech:
- Improved Efficiency and Automation. AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation handle repetitive, time-intensive tasks to boost operational efficiency, leveraging our AI/ML development services to tailor models for finance-specific workflows. Advanced algorithms sift through massive datasets, generate precise forecasts, and execute transactions at speeds and volumes far beyond human capacity. As a result, financial institutions can streamline workflows, cut costs, and optimize resource allocation.
- Enhanced Decision Making. AI systems can process and analyze complex financial data quickly and accurately. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms and pattern recognition, AI can uncover insights, detect trends, and identify potential risks or opportunities. This empowers financial professionals to make well-informed decisions, optimize investment strategies, manage risks, and provide personalized recommendations to clients. The incorporation of AI-driven decisions further enhances the speed, precision, and adaptability of financial decision-making processes in dynamic market environments.
- Personalized Customer Experience. AI algorithms enable personalized and tailored financial services. Virtual assistants and chatbots powered by natural language processing can interact with customers in real-time, providing instant support, answering inquiries, and offering personalized recommendations. This can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Advanced Fraud Detection and Security. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns associated with fraudulent activities, enabling early detection and prevention. AI-powered security systems can continuously monitor transactions, detect anomalies, and alert authorities or customers in real-time, bolstering the overall security of financial operations.
- Simplified Regulatory Compliance. The financial industry is subject to numerous regulations and compliance requirements. AI-powered solutions can automate compliance processes by monitoring transactions, identifying suspicious activities, and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. This helps financial institutions reduce the risk of non-compliance and minimize associated penalties.
Thus, embracing AI technologies can give financial institutions a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. We will look at this in more detail below.
AI Today: Where It Works and What For
For example, in the traveling industry, Artificial Intelligence helps to optimize sales and price, as well as prevent fraudulent transactions. Also, AI makes it possible to provide personalized suggestions for desired dates, routes, and costs, when we are surfing airplane or hotel booking sites planning our next summer vacation. Incorporating a voice AI bot into customer service channels can significantly enhance client interaction and satisfaction.
In the transportation industry, AI is actively employed in the development of self-parking and advanced cruise control features, called to make driving easier and safer. Experts believe that the biggest breakthrough here is around the corner – autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, are already appearing on the roads.
Another bright example of using AI is education where open online courses (MOOC) such as Coursera or Lynda become more and more popular each year. Those have become possible with the rise of Artificial Intelligence in education. Automatic grading made self-taught online courses available for anyone with Internet access – a pivotal point for so many lives and careers.
Artificial Intelligence saves lives, and this is not a figure of speech. From robotic surgeries to virtual nursing assistants and patient monitoring, doctors employ AI to provide their patients with the best care. Image analysis and various administrative tasks, such as filing, and charting are helping to reduce the cost of expensive human labor and allows medical personnel to spend more time with the patients.
The rise of AI in the fintech software development proves how quickly it’s changing the business landscape even in traditionally conservative areas. Here are just some of the most popular examples of AI in finance.
1. AI and Credit Decisions
Artificial Intelligence is widely used in banking apps development as it provides a faster, more accurate assessment of a potential borrower, at less cost, and accounts for a wider variety of factors, which leads to a better-informed, data-backed decision. Alternative credit scoring provided by AI is based on more complex and sophisticated rules compared to those used in traditional credit scoring systems. It helps lenders distinguish between high default risk applicants and those who are credit-worthy but lack an extensive credit history.
Objectivity is another benefit of the AI-powered mechanism. Unlike a human being, a machine is not likely to be biased what is quite important especially in financial app development.
Digital banks and loan-issuing apps use machine learning algorithms to use alternative data (e.g., smartphone data) to evaluate loan eligibility and provide personalized options.
Automobile lending companies in the U.S. have reported success with AI for their needs as well. For example, this report shows that bringing AI on board cut losses by 23% annually.
2. AI and Risk Management
Among the examples of artificial intelligence in banking, it is worth noting this one.
It’s difficult to overestimate the impact of AI in financial services when it comes to risk management. Enormous processing power allows vast amounts of data to be handled in a short time, and cognitive computing helps to manage both structured and unstructured data, a task that would take far too much time for a human to do. Algorithms analyze the history of risk cases and identify early signs of potential future issues. When integrated into AI in ERP platforms, these risk models can trigger automated mitigation workflows across finance and operations.
Artificial intelligence in finance is a powerful ally when it comes to analyzing real-time activities in any given market or environment; the accurate predictions and detailed forecasts it provides are based on multiple variables and vital to business planning.
A US leasing company, Crest Financial, employed artificial intelligence on the Amazon Web Services platform and immediately saw a significant improvement in risk analysis, without the deployment delays associated with traditional data science methods.
3. AI and Fraud Prevention
For a number of years now, artificial intelligence has been very successful in battling financial fraud – and the future is looking brighter every year, as machine learning is catching up with the criminals.
AI is especially effective at preventing credit card fraud, which has been growing exponentially in recent years due to the increase of e-commerce and online transactions. Fraud detection systems analyze clients’ behavior, location, and buying habits and trigger a security mechanism when something seems out of order and contradicts the established spending pattern.
Banks also employ artificial intelligence to reveal and prevent another infamous type of financial crime: money laundering. Machines recognize suspicious activity and help to cut the costs of investigating the alleged money-laundering schemes. One Case study reported a 20% reduction in the investigative workload.
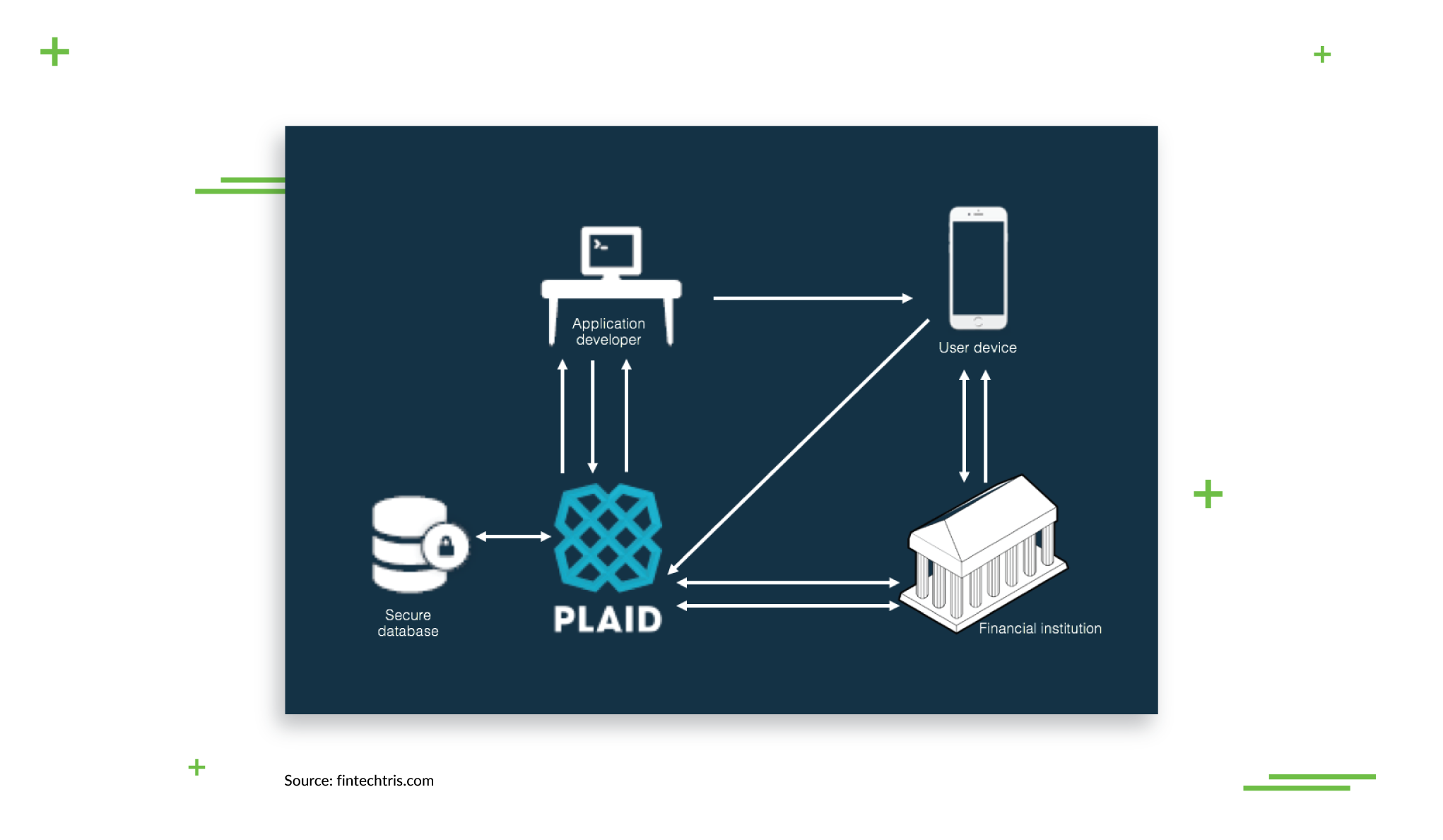
Aggregators like Plaid (which works with financial giants like CITI, Goldman Sachs and American Express) take pride in their fraud-detection capabilities. Its complex algorithms can analyze interactions under different conditions and variables and build multiple unique patterns that are updated in real time. Plaid works as a widget that connects a bank with the client’s app to ensure secure financial transactions.
4. AI and Trading
Data-driven investments have been rising steadily over the last 5 years and closed in on a trillion dollars in 2018. It’s also called algorithmic, quantitative or high-frequency trading.
This kind of trading has been expanding rapidly across the world’s stock markets, and for good reason: artificial intelligence offers multiple significant benefits.
Intelligent Trading Systems monitor both structured (databases, spreadsheets, etc.) and unstructured (social media, news, etc.) data in a fraction of the time it would take for people to process it. And nowhere is the saying “time is money” truer than in trading: faster processing means faster decisions, which in turn mean faster transactions.
The predictions for stock performance are more accurate, due to the fact that algorithms can test trading systems based on past data and bring the validation process to a whole new level before pushing it live.
AI puts together recommendations for the strongest portfolios depending on a specific investor’s short- and long-term goals; multiple financial institutions also trust AI to manage their entire portfolios.
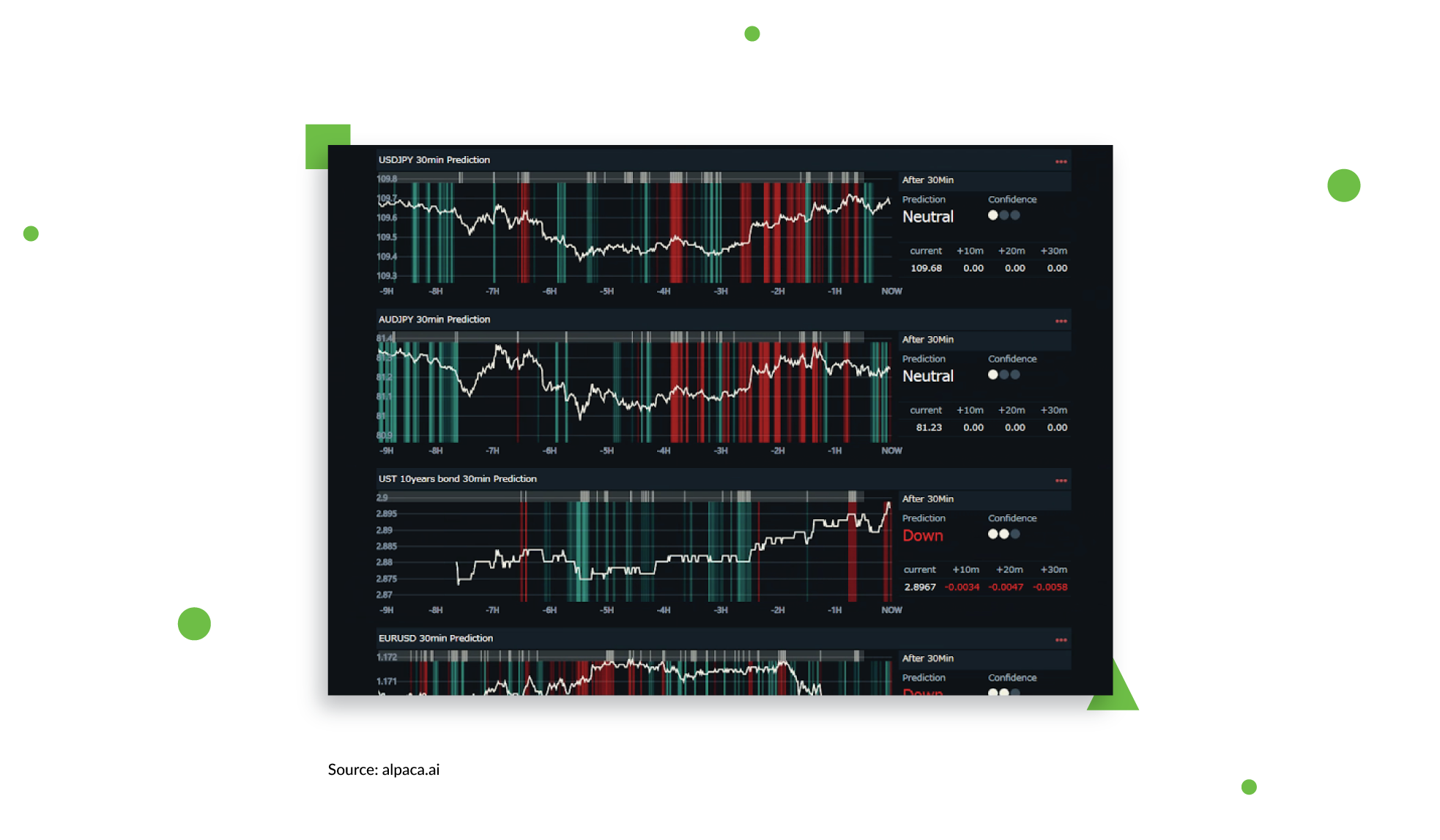
The business news outlet, Bloomberg, recently launched Alpaca Forecast AI Prediction Matrix, a price-forecasting application for investors powered by AI. It combines real-time market data provided by Bloomberg with an advanced learning engine to identify patterns in price movements for high-accuracy market predictions.
5. AI and Personalized Banking
AI for personal finance truly shines when it comes to exploring new ways to provide additional benefits and comfort to individual users.
In the banking sector, AI powers the smart chatbots that provide clients with comprehensive self-help solutions while reducing the call-centers’ workload. Voice-controlled virtual assistants powered by smart tech like Amazon’s Alexa are also gaining traction fast, which is no surprise: boasting a self-education feature, they get smarter every day, so you should expect tremendous improvements here. Both tools can check balances, schedule payments, look up account activity and more.
A number of apps offer personalized financial advice and help individuals achieve their financial goals. These intelligent systems track income, essential recurring expenses, and spending habits and come up with an optimized plan and financial tips.
The biggest US banks, such as Wells Fargo, Bank of America and Chase, have launched mobile banking apps that provide clients with reminders to pay bills, plan their expenses and interact with their bank in an easier and more streamlined way, from getting information to completing transactions.
6. AI and Process Automation
Forward-thinking industry leaders look to robotic process automation when they want to cut operational costs and boost productivity.
Intelligent character recognition makes it possible to automate a variety of mundane, time-consuming tasks that used to take thousands of work hours and inflate payrolls. Artificial intelligence-enabled software verifies data and generates reports according to the given parameters, reviews documents, and extracts information from forms (applications, agreements, etc.).
Employing robotic process automation for high-frequency repetitive tasks eliminates the room for human error and allows a financial institution to refocus workforce efforts on processes that require human involvement. Ernst & Young has reported a 50%-70% cost reduction for these kinds of tasks, and Forbes calls it a “Gateway Drug To Digital Transformation”.
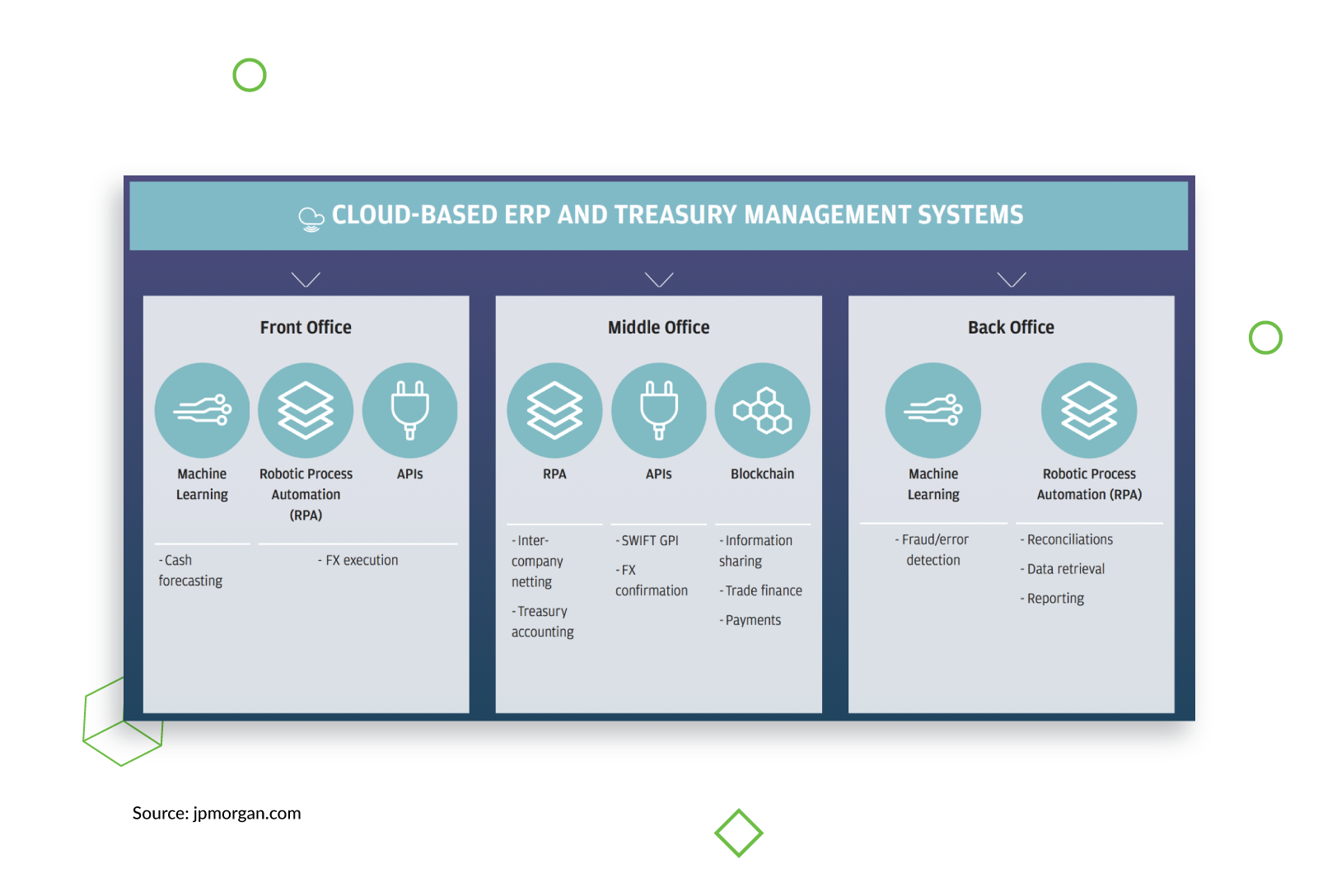
A leading financial firm, JP Morgan Chase, has been successfully leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for a while now to perform tasks such as extracting data, comply with Know Your Customer regulations, and capture documents. RPA is one of ‘five emerging technologies‘ JP Morgan Chase uses to enhance the cash management process.
What to Expect in The Future From AI in the Financial Industry
Predictions for the soon-to-come AI applications in financial services is a hot topic these days but one thing is for sure: AI is rapidly reshaping the business landscape of the financial industry.
There are high hopes for increased transactional and account security, especially as the adoption of blockchains and cryptocurrency expands. In turn, this might drastically reduce or eliminate transaction fees due to the lack of an intermediary. In this regard, AI and financial services show great promise.
All kinds of digital assistants and apps will continue to perfect themselves thanks to cognitive computing. This will make managing personal finances exponentially easier, since the smart machines will be able to plan and execute short- and long-term tasks, from paying bills to preparing tax filings.
We can also expect to see better customer care that uses sophisticated self-help VR systems, as natural-language processing advances and learns more from the expanding data pool of past experience.
A new level of transparency will stem from more comprehensive and accurate know-your-client reporting and more thorough due-diligence checks, which now would be taking too many human work hours.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Banking and Finance
With all the many benefits that the above examples of AI in banking demonstrate, there are also rough edges to consider.
- One of the most notable challenges is ensuring AI algorithms’ accuracy and reliability, as they rely heavily on quality and diverse data for training.
- Privacy concerns and regulatory compliance pose another hurdle, as the use of sensitive financial data requires robust security measures and adherence to strict regulations.
- Also, the complexity of integrating AI systems with existing infrastructure and legacy systems can be a challenge.
- What’s more, AI models may lack transparency, making it challenging to explain their decisions and potentially raising ethical concerns.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing monitoring, continuous improvement, robust data security measures, proactive regulatory compliance efforts, and ethical considerations to ensure the responsible use of AI in finance.
How to implement AI in your financial services organization?
Implementing AI for financial services requires careful planning and execution. This involves a number of important points.
- Strategy development. At the initial stage, it’s necessary to determine specific areas where AI can add value, such as fraud detection, risk assessment, customer service, or investment analysis.
- Choice of technologies. The selection of AI tools, such as machine learning, natural language processing, or robotic process automation, should align with the defined goals and objectives.
- Data preparation. Gathering relevant data from various sources and ensuring its quality and accuracy is essential. The data must be properly cleansed and preprocessed to prepare it for AI algorithms.
- Development of models. The quality of AI models heavily relies on the collected data. Employing ML techniques enables the training of models for specific tasks like credit scoring or portfolio optimization.
- Integration. When incorporating AI models into existing systems and processes, the aim is to achieve smooth interaction between AI systems and human employees.
- Monitoring and refining. It’s crucial to continuously monitor AI performance, identify areas for improvement, and refine models and algorithms accordingly.
- Regulatory compliance. The financial company needs to stay informed about regulations and ensure that AI in finance aligns with legal and ethical guidelines.
Being an iterative process, the implementation of AI for finance requires close collaboration between technology experts, domain specialists, and business stakeholders to achieve the desired outcomes. Consider contacting Django Stars if you would like to involve a reliable tech partner that can provide valuable expertise and guidance throughout the implementation process.
Conclusion
As we can see, the benefits of AI in financial services—powered by AI-driven decision making—are multiple and hard to ignore. According to Forbes, 65% of senior financial management expects positive changes from the use of AI in financial services.
This said, as of late 2018, only a third of companies have taken steps to implement artificial intelligence into their company processes. Many still err on the side of caution, fearing the time and expense such an undertaking will require –, and there will be challenges to implementing AI in financial services.
However, one can’t shy away forever from technological progress and not facing it now may cost more in the long run.
- How AI can improve the banking sector?
- AI can enhance customer service by providing personalized experiences and quicker response times. AI-powered chatbots can handle customer inquiries efficiently. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of data to detect fraud and enhance security measures. Also, it can help banks offer tailored financial products and services. Additionally, AI can automate manual tasks, improving operational efficiency, and AI-powered predictive analytics can aid in risk assessment and loan approvals.
- How does AI improve customer service in financial services?
- AI contributes to providing personalized and efficient experiences through AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated tasks. It offers quick and accurate responses to customer inquiries, learns from interactions, and provides tailored recommendations based on customer data. Also, automation can free up customer service representatives for more specialized inquiries. All this helps make financial services faster and more effective leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- How do AI-based credit scoring and loan underwriting work?
- They enable to automate the process of assessing creditworthiness. By analyzing extensive data, including credit history and financial factors, AI generates predictive models to evaluate risk and repayment likelihood. This technology improves efficiency, reduces bias, and enables faster and more accurate lending decisions. Thus, it widens access to credit and enhances the inclusivity of credit assessments.
- What are the risks associated with using AI for financial services?
- The risks include potential data breaches, algorithmic biases, and regulatory challenges. Data breaches could compromise sensitive customer information, leading to financial loss and reputational damage. Algorithmic biases may result in unfair treatment or discrimination if the AI systems are trained on biased data. Adhering to regulations and ensuring compliance when implementing AI technologies can be challenging due to evolving legal frameworks.