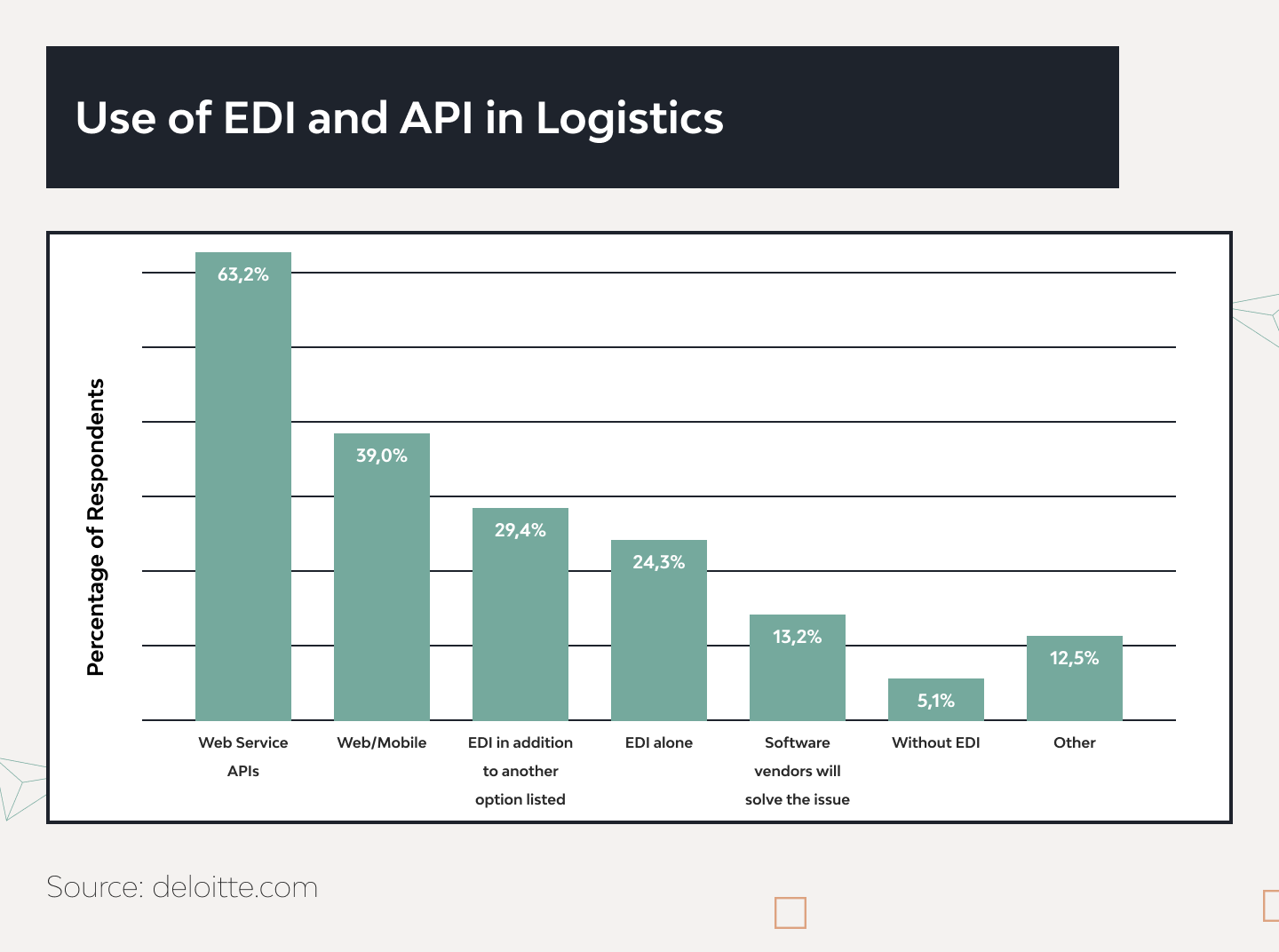
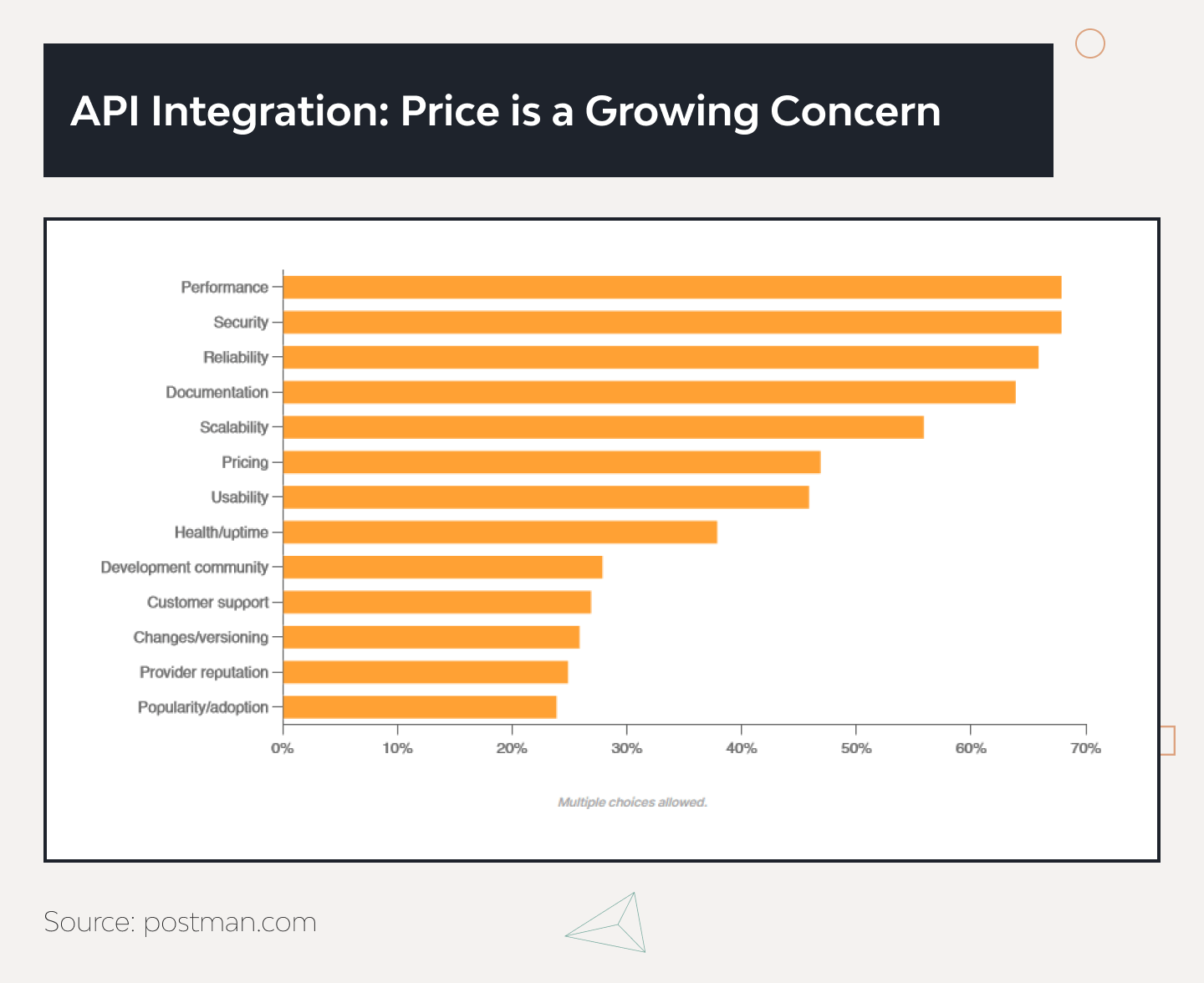
EDI vs API: Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases

In logistics, where timely and accurate delivery requires seamless communication, the role of reliable data exchange systems cannot be overstated. They directly affect key operational aspects such as order processing, real-time tracking, and overall supply chain coordination, which can be streamlined with inventory and shipping management software. And when it comes to customer satisfaction and cost efficiency, every minute counts.
Two of the most common technologies facilitating data exchange in modern logistics are electronic data interchange (EDI) and application programming interface (API). While EDI and API are often compared in the context of logistics data exchange, their role extends deeper into the supply chain. For example, modern companies rely on SRM supplier relationship management systems to strengthen collaboration with vendors, streamline procurement, and ensure compliance.
This article examines EDI vs API integration — from improving efficiency to influencing the strategic capabilities of logistics operations. We explore the distinct characteristics, strengths, and limitations of EDI and APIs, providing insights into their significance in today’s transportation and distribution networks. With this knowledge, supply chain professionals can make more informed decisions, choosing the right technology to meet their specific needs and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving industry.
What is EDI integration?
Before answering the question “What does EDI mean in logistics?”, let’s first clarify “What is EDI integration in general?”
Definition:
Electronic Data Interchange or EDI is a data exchange technology using automatic B2B communications. It was designed in the 1970s but is still widely used because it provides solid stakeholder communication. Of course, with the development of modern technologies, EDI solutions principles and procedures have changed, but it remains a global standard for exchanging information in logistics. Moreover, the global market size of EDI solutions estimated at $1.98 billion in 2023 is projected to more than double and surpass $4.52 billion by 2030, increasing at a CAGR of 12.5%.
How it works:
Data formats:
EDI solutions rely on the globally accepted format EDIFACT, but there are also local standards like TRADACOMS in the UK and ANSI X12 in the USA and Canada.
Connectivity:
EDI systems utilize a secure network (for instance, a VAN – value-added network) or use protocols such as AS2 for direct data transfer.
Methodology:
An organization generates a business document (say, an invoice or a purchase order) via its ERP system, translates it into an acceptable format, and sends it to the addressee. Once it is received, the reverse data format translation and subsequent processing of the document take place. Finally, an EDI message is dispatched to the sender to inform them that the document was successfully delivered and processed.
EDI pros:
- Universal adoption. Having been leveraged for over 50 years, it is harnessed by virtually all logistics organizations worldwide.
- Speed and efficiency. Thanks to the absence of manual data entry, the necessary information is quickly transmitted, received, and processed, accelerating business workflows immensely.
- High security. Data transmission protocols and information encryption safely protect sensitive data exchanged between stakeholders.
- Enhanced visibility and traceability. Data tracking and compliance with requirements are easy when electronic documents are integrated with specialized systems.
EDI Cons:
- One-to-one communication. You can use the system for data transmission only between two partners. Adding any new stakeholder requires additional setup and configuration in the system.
- Standardization. You should ensure that the data standards utilized by partners are mutually readable and convertible.
- Sluggishness. Flat-file-based EDI systems rely on scheduled batch data processing, which may cause delays in synchronous communication.
- Significant upfront and ongoing costs. To set up and keep the system going, you should be ready to invest large sums in software, hardware, personnel training, maintenance, updates, and support.
Given these downsides, you can’t blindly opt for EDI; you should consider EDI vs API integration.
What is API integration?
Definition:
Application Programming Interface or API has similar capabilities but uses different techniques to transfer data. It uses a connection between applications, not direct transferring. API is more intuitive because it usually has a more straightforward interface.
There are dozens of such interfaces suitable for API logistic integration, e-commerce, social network interactions, financial activities, logistics, and many other business branches. However, API is sensitive to digital ecosystem integration but is flexible and allows companies to connect with partners and SaaS applications quickly and efficiently.
How it works:
Data formats:
The basic format used by API logistic systems JSON. Plus XML, CSV, and others are also acceptable.
Connectivity:
APIs leverage HTTP/HTTPS protocols for connectivity, but can also employ more specific systems like REST and SOAP.
Methodology:
A client application sends a request to the server application that contains both an indication of the action to be performed and the necessary data parameters. The API functions as a go-between translating the request into a format understandable to the server. The latter performs the required action (retrieving data, sending information, etc.) and returns a response to the with the results and a status code (successful or failed). API forwards the message further to the client.
API pros:
- Interoperability. No matter the underlying platform, versatile digital systems and applications can exchange data via API.
- High speed. APIs are ideal for fast, direct, and synchronous interaction between IT systems.
- Wide integration possibilities. API logistics integration paves the way for marrying a wide range of software that organizations in the industry leverage in their pipeline activities, including ERP, CRM, warehouse management systems, supply chain platforms, and more.
- Improved user experience. Thanks to APIs, you can integrate multiple services into a single app.
API cons:
- Complexity and compatibility. When you try to integrate multiple APIs, managing their various versions, data formats, and authentication mechanisms can be quite challenging.
- Dependency on third parties. If you onboard APIs from external providers, you become subject to their downtime, functionality transformations, or service termination.
- Security. If inadequately designed and implemented, APIs are exposed to data leakages, unauthorized access, broken authentication, and other security risks and vulnerabilities.
- Limited customization. APIs with pre-wired functionalities may not align with specific requirements.
EDI vs API: Key Differences, Pros and Cons
So, what is the difference between EDFI and API exactly? Let’s deal with the pluses and minuses of both ways of data exchange. Although EDI and API integration are used for similar purposes, the ways data is transmitted are different. Adopting EDI vs API has its pros and cons. You can determine EDI vs API differences and see which way best fits your big data needs by analyzing each.
Even though the API vs EDI technology appeared later, there is no definite answer to which one is better for logistics businesses. Many influential market players still use EDI and are going to keep everything the same.
Let’s compare EDI vs API technologies across several vital criteria for logistics companies.
| Characteristic | EDI | API |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Lower due to batch-oriented data processing through VANs | Higher due to real-time, synchronous, on-demand data exchange |
| Cost | Higher because of hardware, software, and setup expenditures | Lower, but may be significant for custom integrations |
| Flexibility | Limited, since it relies on highly standardized data formats | Greater, since data formats here allow for more versatility |
| Security | Higher, as the connection across closed networks is allowed only between two authorized users | Requires additional measures as APIs are exposed over the internet |
| Expertise | Implementation requires competence in EDI standards, EDI translators, communication protocols, and data mapping | Implementation requires competence in programming languages, web technologies, API design, and cloud platforms |
| Data Size | Large batches of highly standardized data | Small sets of real-time data in human-readable formats |
| Use Cases | Sending structured business documents like purchase orders, shipping manifests, and invoices in retail, logistics, and manufacturing | Scenarios where instant communication and updates are vital (shipment tracking, payment processing) in e-commerce and logistics |
Since logistics companies are in a win-win situation here, it is pivotal to understand when to prefer API vs EDI, or vice versa, in the digital ecosystems they leverage.
Factors to Consider when Choosing between EDI and API Integration
The choice is quite difficult. That’s why we designed a step-by-step checklist containing the top considerations EDI vs API integration requires to help you understand what kind of system would be better for your logistics company.
- Determine the data types you need to share with contractors. EDI is a perfect choice for sharing standardized data like invoices, payment data, shipment information, etc. API is way better for exchanging unstructured data (images or text descriptions).
- Evaluate the existing infrastructure. As EDI vs API pros and cons show, both systems require specific software. Switching between EDI and API when all processes are established is pricey and inconvenient for all parties. But still, you may combine separate elements into a solid and variable ecosystem.
- Consider the difficulties of tool adoption. EDI requires highly specialized expertise to implement. If you have limited technical resources, it’s better to pick API tools.
- Calculate the price. The price difference between EDI vs API solutions is significant. EDI solutions are usually expensive, especially for extensive facilities. Still, API adoption may also be pricey — it all depends on the difficulty of tasks and the level of integration into a supply chain. Nevertheless, point API solutions may be affordable even for small businesses.
- Consider the system’s flexibility. EDI is strictly standardized, so its customization for unusual tasks may be limited. If you want more operational freedom, choosing API solutions is better.
- Determine the required security level. Experts don’t recommend using API to exchange the most sensitive data because system leaks may compromise the entire ecosystem. EDI tools are considered safer to use, but they still depend on system features and support.
- Find out the scalability options needed. API systems are easily scalable, so even if a company is growing fast, it wouldn’t be a problem. EDI tools are much less flexible and may require significant resources to enhance.
- Check the required technical expertise. EDI and API integration require a completely different technology stack and experience. Moreover, API tools are still updating and changing, so adopting them may require additional resources to improve the system. Before opting for either, make sure the implementation team is competent in the core technologies EDI or API are developed with.
- Can EDI and API integration be used together?
- Yes. they can. A combination of EDI and API may provide a profitable solution for logistics companies. For example, EDI may be used for transferring payment information, invoices, and sensitive data, and API — for exchanging other types of files or designing real-time data transmitting processes.
- How long does it take to implement EDI or API integration?
- It greatly depends on the complexity of the chosen solution. Implementing full-fledged EDI tools may take from 3 to 6 months. Still, complicated API solutions may require lots of time to deploy, but point ones may be integrated in days.
- What are the top considerations when choosing between EDI and API?
- When choosing between EDI vs API, the key factors are the data types you need to transmit, your current infrastructure and its flexibility, tool adoption issues, scalability requirements, the necessary security level, the availability of technical expertise, and, of course, the cost.
- What is the best approach for data integration: EDI or API?
- The wise decision is to combine both. EDI should be leveraged for batch processing of standardized files in high volumes, while API is better suited for flexible, real-time integration needs, where continuous updates and instant communication are mission-critical.
- What are the best tools for EDI API integration?
- You can choose between dedicated integration platforms (such as Cleo, MuleSoft, Jitterbit, or Boomi) and industry-specific providers, for instance, TrueCommerce, DCKAP Integrator, OpenText, IBM Sterling, or SPS Commerce. The ultimate choice is conditioned by your business needs, scalability requirements, and available budget.