How to Create & Pitch Prototype for Your Startup

Creating effective prototypes is a critical challenge for healthcare startups, often fraught with uncertainty about the best practices, processes, and presentation skills required.
This article addresses these pain points, guiding you through startup prototyping from the basics to making your prototype appealing to investors. We’ll cover everything from the differences between web and mobile prototypes to how to find developers for your startup to create a prototype and key strategies for a successful investor pitch.
Prototyping is essential for startups to visualize their concepts, gather early feedback, reduce development costs, and attract investors. This comprehensive guide will help you understand and navigate the complexities of prototyping, enhance your presentation skills, and effectively differentiate between web and mobile versions.
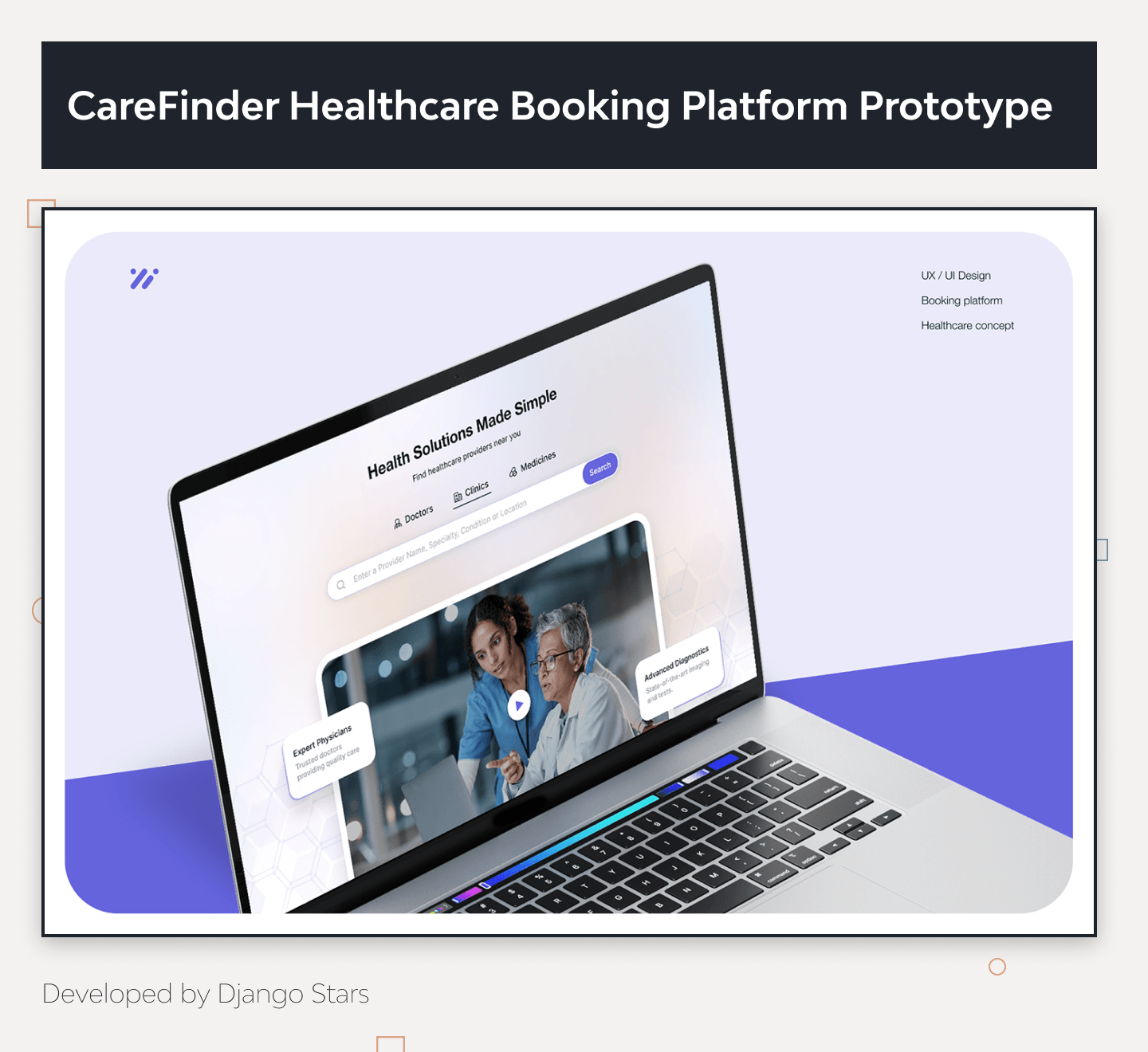
For practical insights and examples of prototypes, check out our CareFinder Healthcare Booking Platform prototype, developed by our company.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to create impactful prototypes and convincingly present them to investors, supported by real-world examples and expert tips from Django Stars.
Why Prototypes Are a Startup’s Best Bet
Startup prototype examples help you visualize your concept, get feedback early, save money, and attract investors. Here’s why prototypes are essential.
Visualizing Concepts
To create a prototype of the startup means to turn your idea into something tangible. It helps you and others see what the final product might look like. This makes it easier to explain and understand your vision.
Early Feedback and Iteration
Startup prototype is important to get feedback early on. You can show it to potential users and stakeholders to see what they think. This feedback helps you make improvements before you spend too much time and money.
Reducing Development Costs
By identifying problems early with a prototype, you can avoid expensive changes later. It helps you focus your resources on what works and fix what doesn’t before full-scale development.
Attracting Investors
Investors want to see that your idea can work. A prototype for a project shows them exactly what you’re planning. It demonstrates your capability and makes your pitch more compelling.
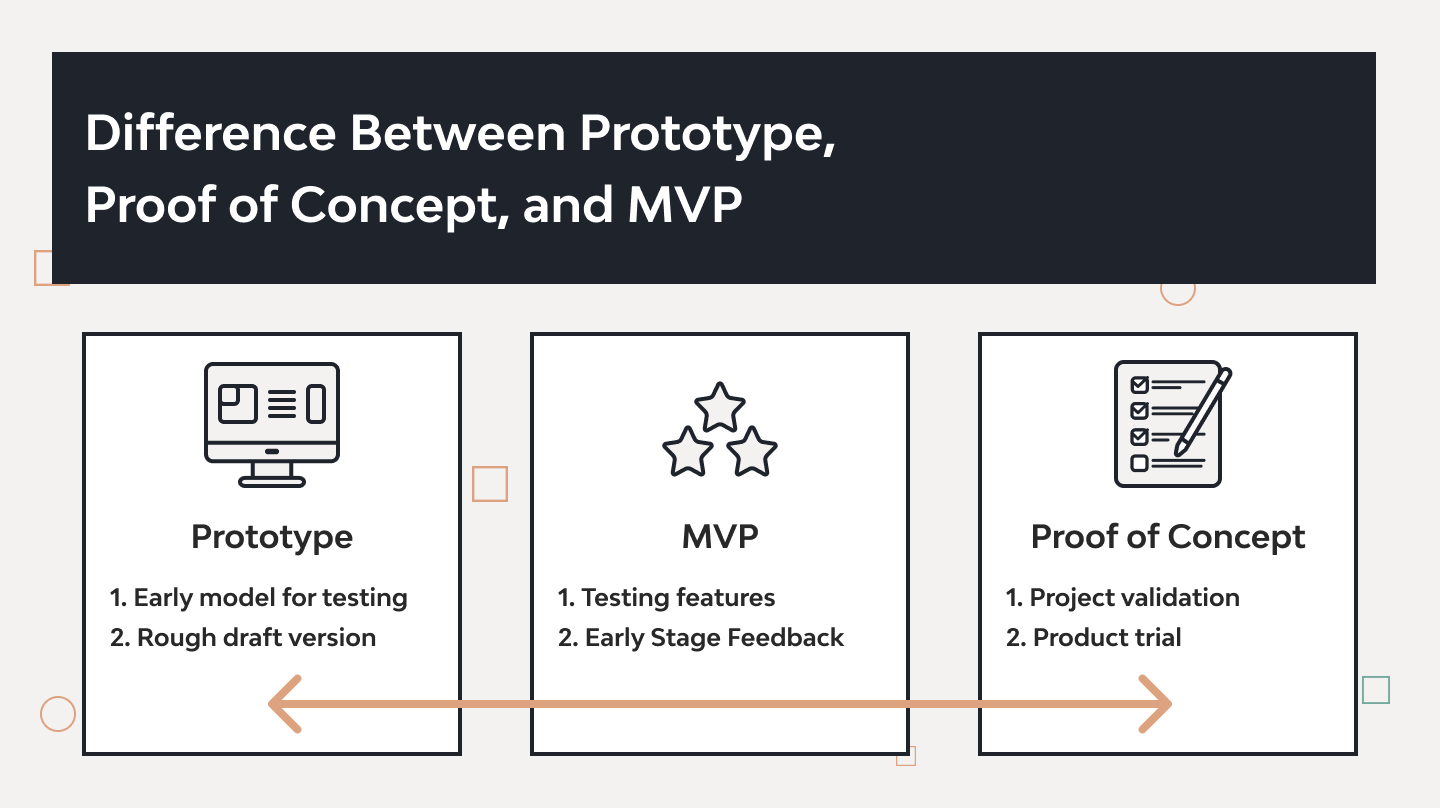
Difference Between Prototype, Proof of Concept, and MVP
Here’s a table to clarify the differences:
| Aspect | Prototype | Proof of Concept (PoC) | Minimum Viable Product (MVP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Show the look and feel of the product | Test if an idea is feasible | Launch with essential features |
| Stage | Early development | Idea validation | Pre-launch |
| Scope | Focus on design and basic functionality | Technical feasibility | Core functionalities |
| Audience | Stakeholders, early users | Internal team | Early customers |
| Investment | Moderate | Low | High |
| Feedback | Design and user experience insights | Feasibility feedback | Market feedback |
Must-Have Elements of an Effective Prototype
If you’re wondering how to build a startup prototype, make sure it includes the following:
Functionality
Demonstrate the main features of your product. Show how it will solve the problem it’s designed to address.
User Interface (UI)
Make the UI clean and easy to navigate. It should look good and be simple for users to understand.
User Experience (UX)
Ensure the prototype provides a smooth experience. Think about the user journey and make it enjoyable and efficient.
8 Steps to Create an Effective Prototype
Creating an effective prototype is essential for any startup, especially in healthcare. Here’s a step-by-step guide with examples to help you build a prototype for a startup and avoid common pitfalls.
Step 1. Define Your Objectives
What You Need to Do:
- Clearly outline what you want to achieve with your prototype.
- Identify the key features and functionalities that need to be demonstrated.
Example: A healthcare startup developing a telemedicine app might set objectives to showcase video calling functionality, appointment scheduling, and secure patient data management.
Pitfall: Starting without clear goals can lead to unfocused startup prototype development, which can waste time and resources.
Step 2. Conduct Market Research
What You Need to Do:
- Understand your target audience and their needs.
- Analyze competitors and identify gaps in the market.
Example: Research shows that existing telemedicine apps lack easy integration with wearable health devices. Your prototype will address this gap by incorporating this feature.
Pitfall: Skipping market research. The prototype stage startup may not meet user needs, reducing its chances of success.
Step 3. Choose the Right Tools
What You Need to Do:
- Select tools that best suit your prototype’s needs. Popular options include Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD for design, and InVision or Axure for adding interactivity.
Example: Using Figma for design and InVision for adding interactive elements like clickable buttons and navigation flows.
Pitfall: Using the wrong tools for design and interactivity. This can lead to inefficiencies and a subpar prototype.
Step 4. Create a Wireframe
What You Need to Do:
- Start with a basic wireframe to map out the structure and layout of your prototype.
- Focus on the placement of key elements and overall navigation flow.
Example: Creating a wireframe that outlines the main screens of the telemedicine app, including the login page, dashboard, video call interface, and appointment scheduling.
Pitfall: Jumping straight into detailed design without a wireframe. This can result in a disorganized layout and poor user experience.
Step 5. Design the User Interface (UI)
What You Need to Do:
- Develop the visual aspects of your prototype, ensuring it’s attractive and user-friendly.
- Pay attention to color schemes, typography, and overall aesthetics.
Example: Designing a clean and intuitive interface with easy-to-read fonts, calming colors, and clear icons for the app.
Pitfall: Neglecting the visual aspects of the prototype. Users and investors may find the product unattractive or hard to use.
Step 6. Add Interactivity
What You Need to Do:
- Incorporate interactive elements like clickable buttons, navigation flows, and transitions.
- Use tools like InVision or Axure to simulate real user interactions.
Example: Adding clickable buttons for scheduling appointments and starting video calls in startup prototyping.
Pitfall: Failing to add interactive elements. The prototype may not effectively demonstrate functionality, reducing its impact.
Step 7. Test and Iterate
What You Need to Do:
- Conduct usability testing with a small group of users.
- Gather feedback and identify areas for improvement.
- Refine and iterate based on the feedback received.
Example: Testing the telemedicine app prototype with a group of doctors and patients, then making adjustments based on their feedback, such as simplifying the appointment scheduling process.
Pitfall: Not testing the prototype with real users. Unidentified issues can lead to a flawed final product.
Step 8. Prepare for Presentation
What You Need to Do:
- Create a compelling narrative around your prototype.
- Prepare a pitch that highlights the problem, solution, and benefits.
- Practice presenting your prototype to ensure a smooth delivery.
Example: Developing a pitch that tells the story of a patient who struggles to find convenient healthcare, and how your telemedicine app solves this problem by providing easy access to doctors.
Pitfall: Not preparing a compelling pitch. The prototype may fail to attract investor interest, hindering funding opportunities.
Why Choose Django Stars for Your Startup Prototyping
When it comes to developing prototypes, especially for healthcare startups, selecting a partner with the right expertise and experience is crucial. Django Stars stands out in the field with its comprehensive digital product design services, tailored to help startups create impactful and user-centered prototypes. Here’s how Django Stars can assist in bringing your healthcare innovation to life:
Expertise in Digital Product Design
Django Stars has a proven track record with over 60 design projects, including collaborations with Y Combinator startups and Fortune 500 companies. Our experience spans the entire product design lifecycle, from idea to prototype, ensuring that your project is both visually stunning and functionally effective.
Comprehensive Prototyping Services
Our prototyping services are designed to help clients identify efficient product design solutions that offer clear value propositions and drive user engagement. By iterating on prototypes, we gather valuable data and hidden insights, reduce time-to-market, and shape the final product in a predictable, data-driven way.
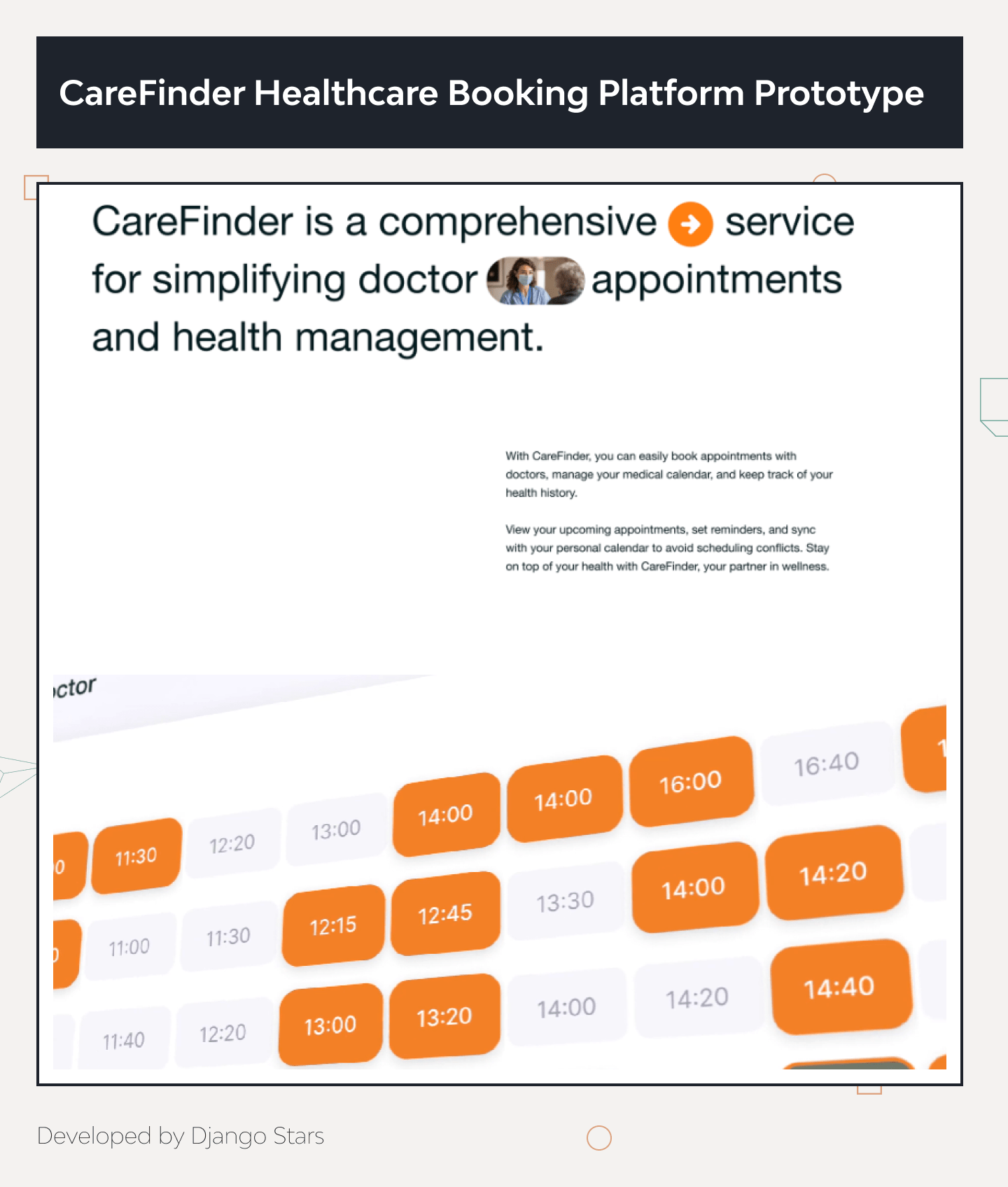
Example: CareFinder Healthcare Booking Platform
One of our standout projects is the CareFinder healthcare booking platform prototype. This project demonstrates our ability to create a seamless and user-friendly interface for healthcare services.
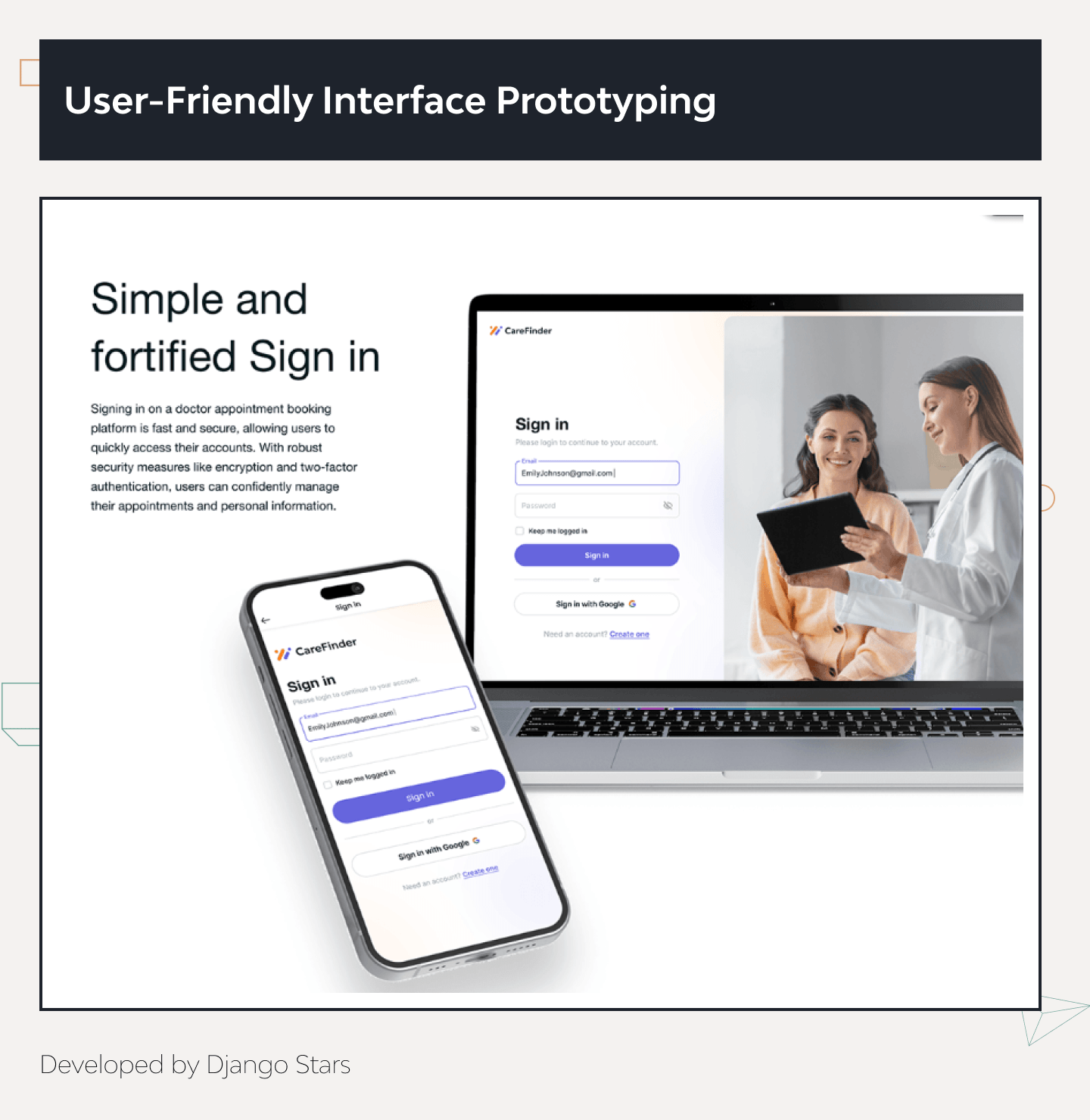
User-Friendly Interface
The CareFinder prototype features a clean and intuitive interface, making it easy for users to book appointments and manage their healthcare needs.
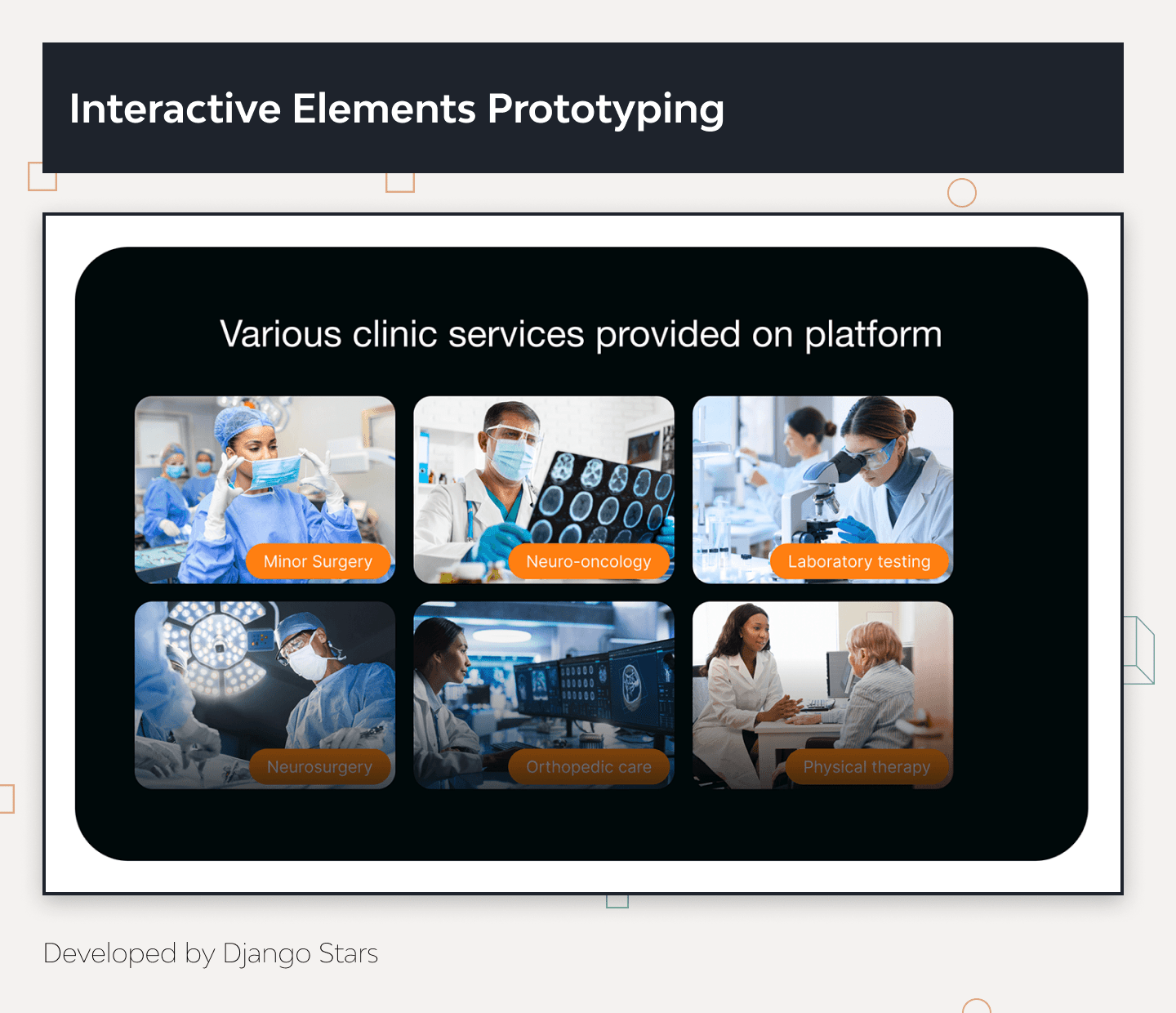
Interactive Elements
The prototype includes interactive elements like clickable buttons and navigation flows, simulating real user interactions and providing a realistic experience of the final product.
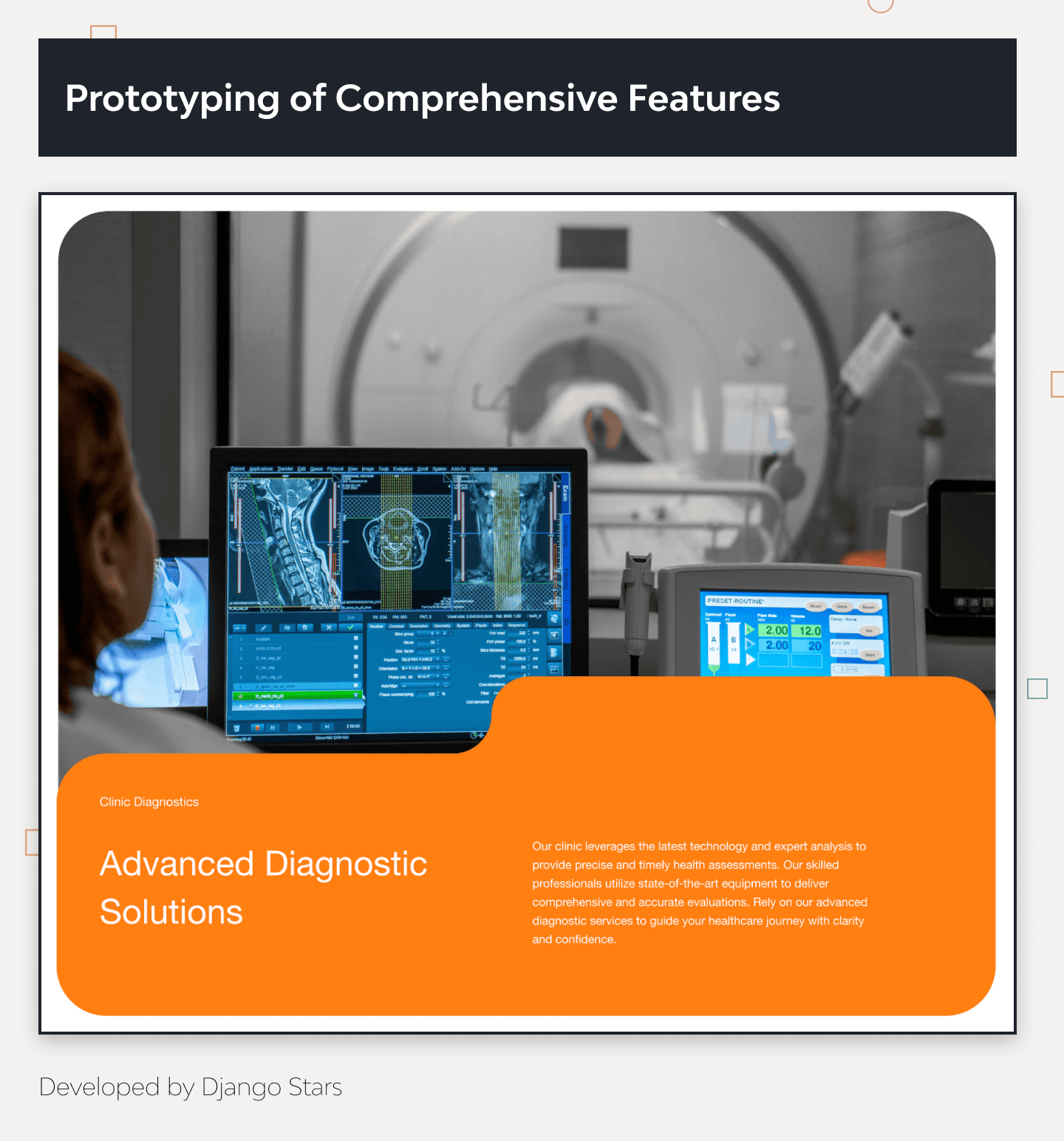
Comprehensive Features
It showcases essential functionalities such as appointment scheduling, doctor profiles, patient reviews, and secure data handling, demonstrating our ability to integrate complex features seamlessly.
The Django Stars Prototyping Process
Our digital product design process ensures that we create user-centered products that are both visually compelling and functionally robust. Here’s a detailed look at our approach:
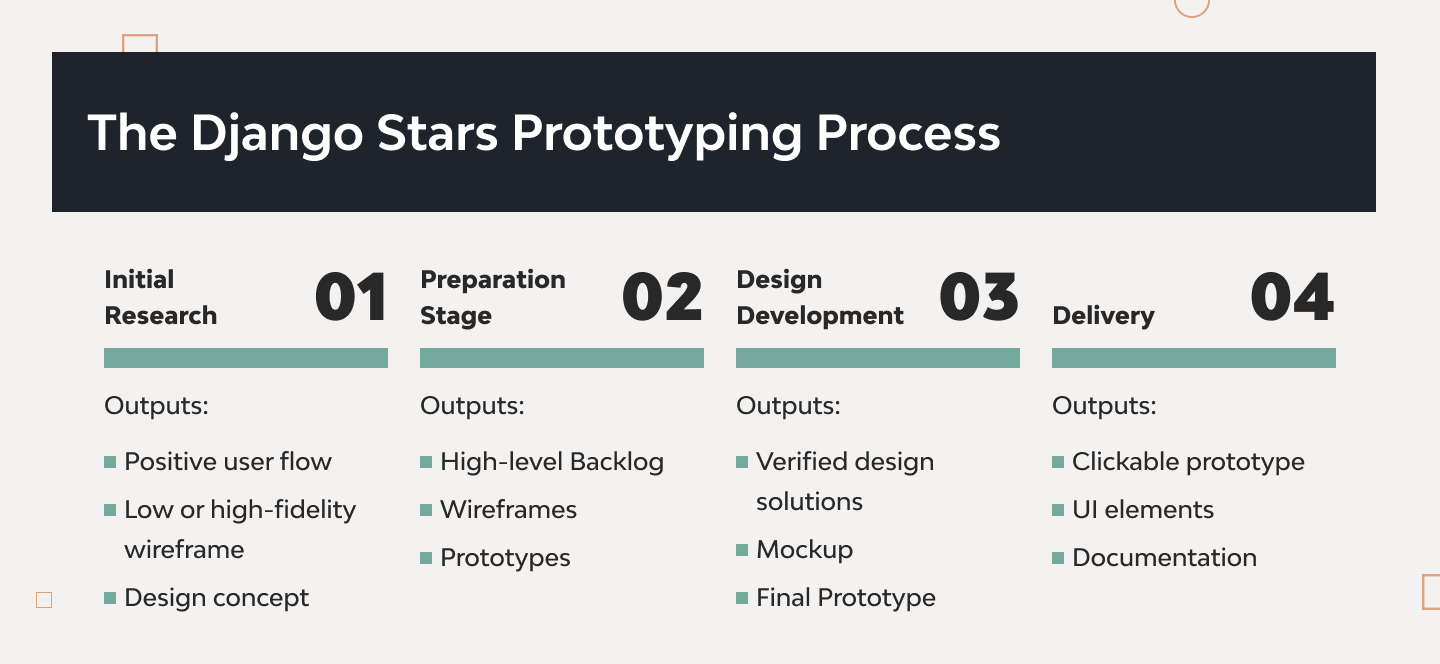
Initial Research
This stage involves collecting information about the product, market, and audience. We define user personas, create customer journey maps, and outline user scenarios.
Example: For a telemedicine app, we would research patient and doctor needs, competitive landscape, and regulatory requirements to create detailed user personas and journey maps.
Outputs:
- Positive user flow
- Low or high-fidelity wireframe
- Design concept
Preparation Stage
We identify pain points, shape the user flow, and develop styles. Through iterative wireframing and prototyping, we refine the design solutions.
Example: Creating wireframes for different user interactions in the telemedicine app, like booking appointments and conducting video consultations.
Outputs:
- High-level Backlog
- User flow
- Wireframes
- Mockups
- Prototypes
Design Development
We create final artifacts, including full user flows, improved wireframes, UI styles, and compliance-verified interfaces.
Example: Developing a polished user interface for the telemedicine app that is easy to navigate and meets regulatory standards.
Outputs:
- Verified design solutions
- Mockup
- Final Prototype
Delivery
We finalize our developments and deliver all design artifacts to ensure the product is easy to maintain and improve.
Example: Handing over the complete design package for the telemedicine app, including all UI elements, interaction guidelines, and documentation.
Startup Success Stories
Our clients’ success stories highlight our expertise and dedication. Startups we have worked with have successfully secured funding, launched their products, and made significant impacts in the industry. For detailed case studies, visit:
By choosing Django Stars for your startup prototyping, you gain access to a team with deep industry knowledge, technical expertise, and a commitment to user-centric design. Our comprehensive approach ensures that your prototype showcases your vision and meets the highest standards of functionality and usability.
Differentiating Between Web and Mobile Prototypes
When creating prototypes for startups, especially in the healthcare sector, it’s crucial to understand the differences between web and mobile. Each platform has unique requirements and user interaction patterns that must be addressed to create effective and engaging prototypes.
Here’s a detailed table outlining the considerations for web experience startup prototyping versus mobile versions:
| Aspect | Web Prototypes | Mobile Prototypes |
|---|---|---|
| Screen Sizes | Wide range (e.g., 1024x768 to 1920x1080+) | Smaller screens (e.g., 375x667, 414x896) |
| User Interaction | Mouse and keyboard interactions | Touch interactions (tap, swipe, pinch) |
| Navigation | Complex menus, multi-level navigation | Simplified navigation, bottom bars, hamburgers |
| Content Layout | More content, multiple columns | Concise, single-column layouts |
| Performance | Can handle data-intensive features | Optimized for lower processing power |
| Responsiveness | Must be responsive to various screen sizes | Primarily focused on mobile screen sizes |
| Design Complexity | Higher complexity possible | Needs to be simplified for ease of use |
| Interaction Feedback | Hover effects, detailed feedback | Immediate touch feedback, less hover |
| Accessibility | Keyboard navigation, screen reader support | Voice commands, screen reader compatibility |
| User Context | Stationary use, longer sessions | On-the-go use, shorter sessions |
| Connectivity | Generally stable and fast connections | Varies, needs to handle offline mode |
Detailed Considerations
Screen Sizes
Web Prototypes: Designers must create flexible layouts that adapt to different screen sizes, ensuring usability across a range of devices, from small laptops to large monitors.
Mobile Prototypes: Designs should fit well on smaller screens, maintaining readability and usability even on devices with lower resolutions.
User Interaction
Web Prototypes: Users interact with web applications using a mouse and keyboard, allowing for more precise actions and complex interactions.
Mobile Prototypes: Interactions are touch-based, requiring larger touch targets and intuitive gestures to ensure a seamless user experience.
Navigation
Web Prototypes: Can incorporate complex navigation structures due to the larger screen size and precise interaction methods.
Mobile Prototypes: Navigation needs to be streamlined, using bottom navigation bars or hamburger menus to save screen space and simplify access to different sections.
Content Layout
Web Prototypes: Can display more content at once, utilizing multi-column layouts and detailed information displays.
Mobile Prototypes: Require more concise layouts, focusing on essential information and minimizing the need for extensive scrolling.
Performance
Web Prototypes: Generally, have more robust hardware and internet connections, allowing for richer, more data-intensive features.
Mobile Prototypes: Need to be optimized for mobile processors and variable internet connectivity, ensuring smooth performance without draining battery life.
How to Pitch Your Startup Prototype Successfully
Pitching your startup prototype model effectively is crucial for attracting investors and securing funding. Here are some essential tips to make your prototyping for startups stand out and ensure a successful pitch.
Key Components of an Investor Presentation
- Problem Statement. Clearly define the problem your product solves. Use data and real-life examples to illustrate the problem’s significance.
- Solution. Demonstrate how your prototype addresses the problem. Highlight unique features and benefits that differentiate your solution from existing alternatives.
- Market Opportunity. Provide data on the target market size and growth potential. Discuss trends and how your solution fits into the current market landscape.
- Business Model. Explain how your product will make money. Include pricing strategies, sales channels, and revenue projections.
- Competitive Analysis. Identify your competitors and outline your competitive advantages. Show why your solution is superior and how it will capture market share.
- Go-to-Market Strategy. Detail your plan for launching and scaling the product. Include marketing tactics, sales strategies, and partnership plans.
- Team. Highlight the strengths and expertise of your team members. Explain why your team is uniquely positioned to execute the business plan.
- Financial Projections. Provide realistic financial forecasts, including revenue, expenses, and profitability. Show how the investment will be used to achieve your business goals.
Tips to Stay Calm During Your Pitch
- Practice Thoroughly. Rehearse your presentation multiple times. Familiarize yourself with the prototype and anticipate potential questions.
- Visualize Success. Picture yourself delivering a successful pitch. Visualization can help reduce anxiety and boost confidence.
- Take Deep Breaths. Practice deep breathing exercises before and during your presentation. Deep breaths can calm your nerves and help you stay focused.
Anxiety can lead to mistakes, such as clicking in the wrong place. To mitigate this risk, record a video of your prototype’s interactivity. This ensures a smooth, error-free demonstration and allows you to focus on delivering your pitch.
Conclusion
Creating and pitching a successful prototype is a critical step for any startup. Prototypes help visualize concepts, gather early feedback, reduce the costs of software development for startups, and attract investors. Each platform has unique requirements, from screen sizes and user interaction patterns to performance considerations and content layout.
Pitch your startup idea. A thorough startup product discovery process should include a clear problem statement, proposed solution, market opportunity, prototyping model, competitive analysis, go-to-market strategy, team overview, and financial projections. Practice thoroughly, visualize success, take deep breaths, and consider recording a video of your prototype’s interactivity to avoid mistakes.
Engage your audience, clarify your vision, and build an emotional connection with investors through compelling storytelling. Investing time and resources in understanding and developing effective prototypes can significantly enhance your startup’s chances of success.
Prototypes are powerful tools for communicating your vision, validating your ideas, and securing the necessary support and funding.
By following these guidelines and investing in a well-crafted prototype, startups can effectively communicate their vision, engage investors, and take significant strides toward bringing their innovative ideas to market.
For more insights and assistance with your prototyping needs, consider partnering with Django Stars. We can guide you through the process and help you achieve your goals.
- How much does it typically cost to create a prototype of the product?
- The cost of developing a startup's prototype can vary widely based on the complexity of the project, the features included, and the development team's expertise. On average, it can range from $10,000 to $50,000.
- When is the best time to showcase a prototype to potential investors?
- The best time to showcase a prototype to potential investors is after you've validated your idea through initial market research and user testing. This means having a functional prototype that demonstrates the core features and user experience.
- What are the best practices for presenting a prototype to potential investors?
- Best practices for presenting a prototype to potential investors include:
- Preparing a compelling pitch that clearly defines the problem and solution
- Using storytelling to engage the audience and highlight the impact of your product
- Recording a video of the prototype's interactivity to avoid technical issues during the presentation
- Practicing thoroughly to ensure a smooth and confident delivery
- Including key components such as market opportunity, business model, competitive analysis, and financial projections
- What other industries do you specialize in besides healthcare for prototype development?
- Besides healthcare, Django Stars specializes in developing prototypes for various industries, including fintech, e-commerce, travel, real estate, and others. Our diverse experience across these sectors allows us to bring unique insights and innovative solutions to each project, ensuring that prototypes are tailored to meet the specific needs of different markets.
- How does rapid prototyping startup help in reducing time-to-market?
- Prototyping helps reduce time to market by allowing startups to test and refine their ideas early in the development process. By identifying and addressing potential issues before full-scale development, prototypes ensure that only well-validated features make it to the final product. This iterative process helps avoid costly rework, speed up the overall development timeline, and ensure a smoother product launch.