nFADP Compliance: What is It and How to Implement in Web Applications

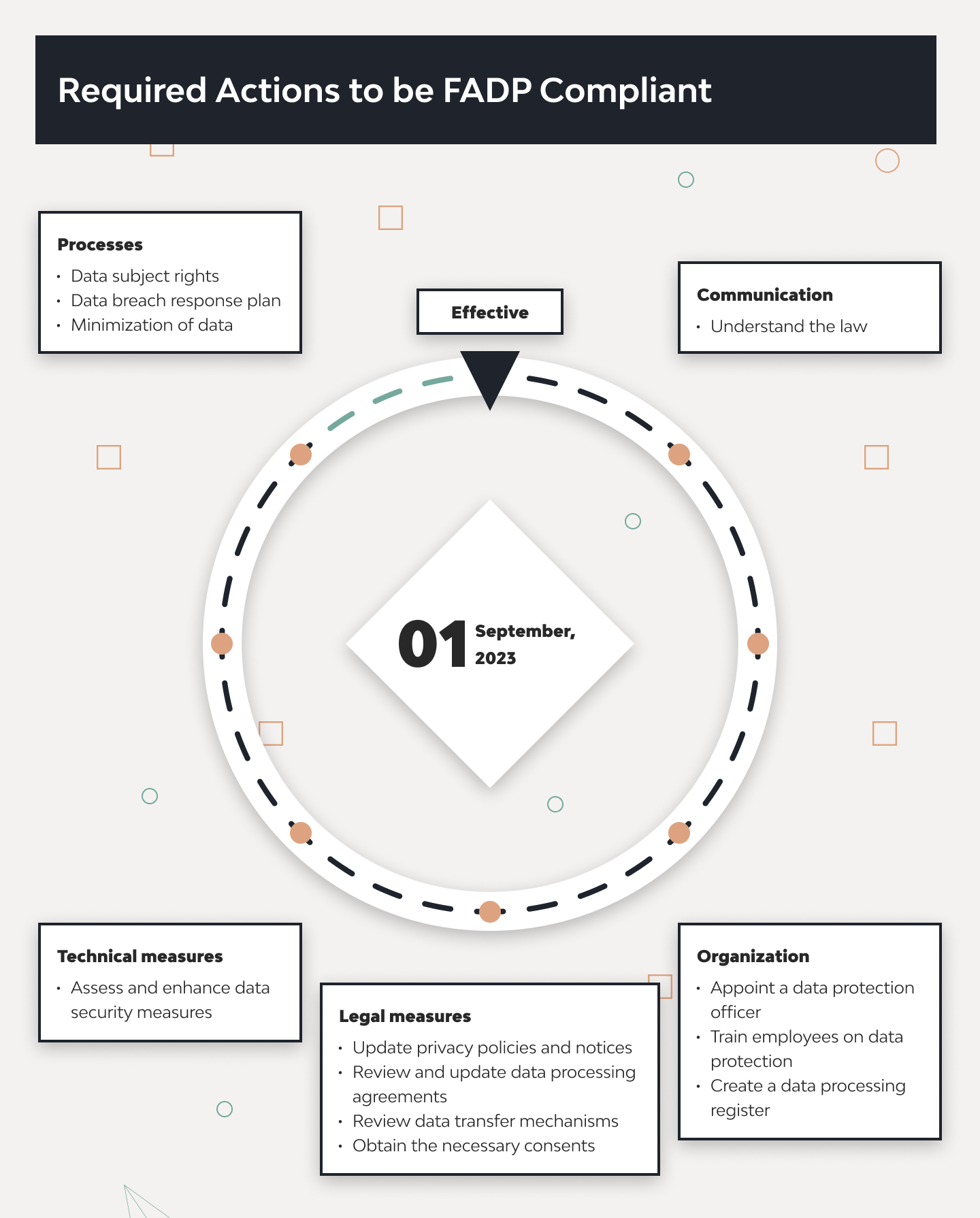
nFADP compliance is a critical concern for organizations operating in Switzerland. The Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (FADP) was established in 1992, and it required a significant update to meet contemporary data privacy needs. This led to the development of the new Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP), set to take effect on September 1, 2023.
This new legislation aims to align Swiss data protection standards with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ensuring that Swiss businesses remain compliant and competitive globally.
By the end of this article, readers will understand:
- The reasons behind updating the FADP and introducing the nFADP
- The main challenges in implementing nFADP compliance
- General requirements and new obligations for businesses under the nFADP
- Steps for implementing nFADP compliance in web applications
- DjangoStars’ approach and experience in achieving compliance with nFADP
- Key strategies for businesses to ensure robust data protection practices
Let’s explore how to comply with the nFADP and enhance data security.
What Is the nFADP?
Switzerland’s new Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP) took effect on September 1, 2023. It represents a significant update to the country’s data protection framework. This legislation aims to modernize and strengthen individuals’ privacy rights by aligning more closely with the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
The Swiss Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner (FDPIC) started the initiative to update Switzerland’s data protection laws, which had been in place since 1992. The primary goal was to align Switzerland’s data protection standards with international norms, particularly the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
The legislative process for the revised Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP) involved extensive consultations and deliberations. Input was gathered from various interest groups, businesses, government entities, and the public. The Swiss Parliament engaged in thorough debates to ensure the new law struck a balance between personal privacy, digital commerce, and security needs.
This extensive process culminated in the law’s passage by the Swiss Parliament, with the new regulations set to take effect on September 1, 2023. Ensuring compliance with nFADP will be essential for organizations operating in Switzerland.
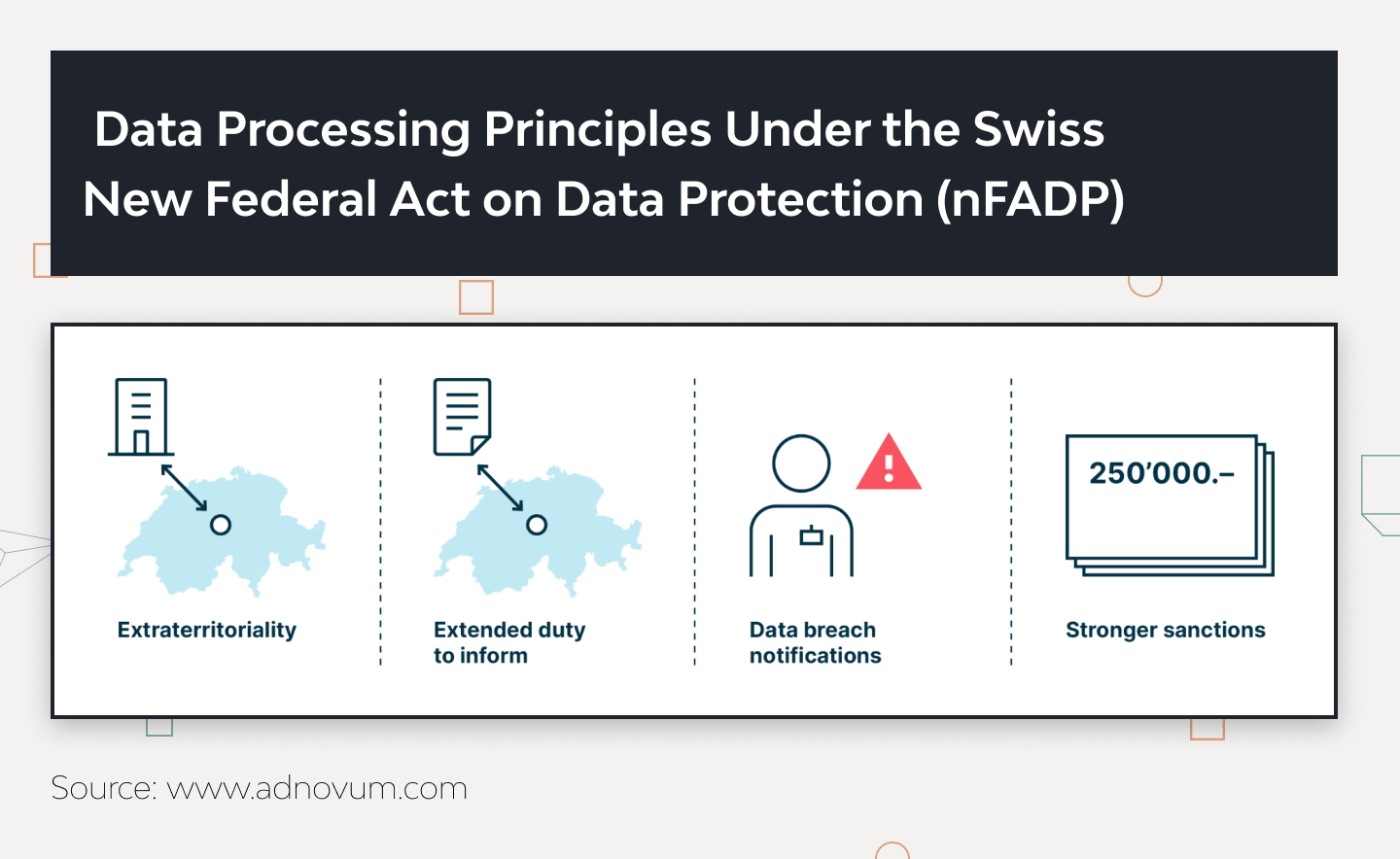
Data Processing Principles Under the Swiss New Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP)
Lawful Processing
Under the nFADP, all data processing activities must have a legal basis. This means that personal data can only be processed if there is a clear legal justification, such as the consent of the data subject, the necessity for the performance of a contract, nFDAP compliance with a legal obligation, protection of vital interests, performance of a task carried out in the public interest, or legitimate interests pursued by the data controller or a third party.
Good Faith and Proportionality
Data processing must be conducted in good faith and proportionate to the purpose for which the data is being processed. This principle ensures that data processing activities are fair, transparent, and not excessive relative to the intended purposes. It also implies that data controllers should not misuse personal data or process more data than necessary.
Specific Purpose
Personal data should only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes and should not be further processed in an incompatible manner. This principle ensures that data subjects know why their data is collected and that their data is not used for unrelated purposes without their consent.
Data Minimization
The principle of data minimization mandates that only the personal data necessary for specific purposes should be collected and processed. This helps reduce the risk of data breaches and ensures that data controllers do not hold excessive amounts of personal data, which might increase privacy risks.
Accuracy
Data controllers must ensure that personal data is accurate and up to date. Inaccurate data should be corrected or deleted without delay. This principle ensures the data’s reliability and protects the data subject from potential harm caused by inaccuracies.
Integrity and Confidentiality
Complying with the nFADP means that personal data must be processed to ensure appropriate security, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction, or damage. Data controllers are required to implement suitable technical and organizational measures to secure personal data and maintain its confidentiality.
The Importance of Complying with the nFADP
Legal Compliance
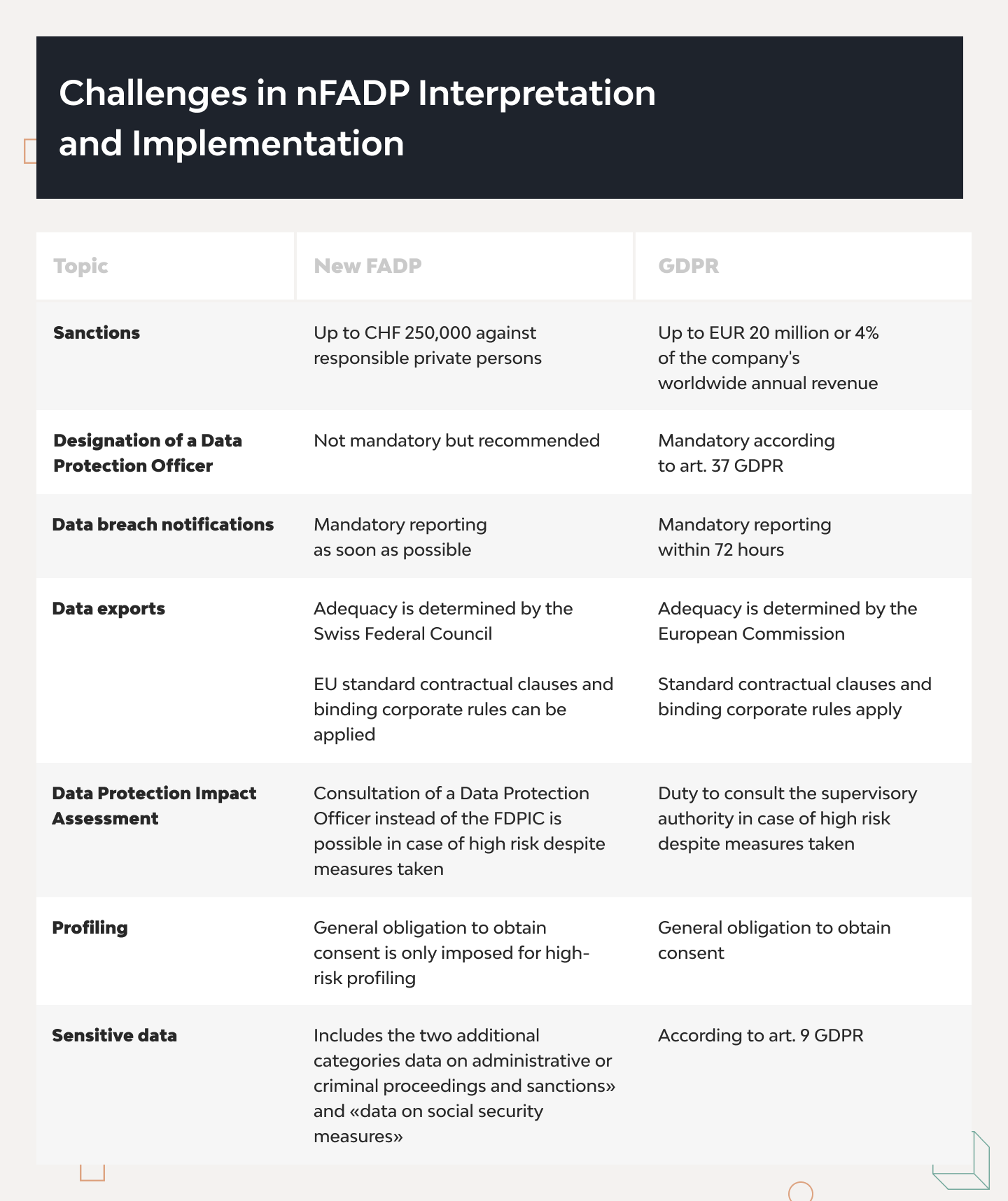
nFADP standard compliance is essential for Swiss companies to avoid legal consequences. The revised law imposes strict obligations on data controllers and processors, and failure to comply can result in substantial fines and penalties. For instance, individuals responsible for intentional violations can face criminal sanctions of up to CHF 250,000, while companies might incur fines if the responsible person cannot be identified.
Building Trust with Customers
Adhering to the nFADP enhances a company’s reputation by demonstrating a commitment to protecting personal data. This makes customers feel more confident and secure, knowing their information is handled correctly. The importance of nFADP compliance is huge, as it reassures customers that the organization is serious about keeping their data safe.
Competitive Advantage
Compliance with the nFADP can provide a competitive edge. Companies that meet high data protection standards are more attractive to partners and customers. This is particularly relevant for businesses dealing with international clients with stringent data protection expectations based on GDPR or similar regulations.
Avoiding Operational Disruptions
Non-compliance with data protection laws can lead to investigations, sanctions, and other legal actions that disrupt business operations. Companies can avoid these disruptions by ensuring compliance with the nFADP and focusing on their core business activities. This proactive data protection approach helps maintain smooth and uninterrupted operations.
Facilitating International Data Transfers
The nFADP is aligned with the GDPR in many aspects, which facilitates international data transfers. Companies compliant with the nFADP are better positioned to engage in business with EU partners and clients, as they can assure these stakeholders that they adhere to comparable data protection standards.
Enhancing Data Security
The nFADP requires companies to implement robust data security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Enhanced data security protects sensitive information and helps maintain the integrity and reliability of business operations.
Challenges in nFADP Interpretation and Implementation
Implementing the nFADP has presented several challenges for Swiss businesses, particularly in interpreting and practically applying the new regulations. These nFDAP challenges stem from the need to adapt to a legislative framework aligned with the GDPR, which has unique nuances and requirements.
Ambiguity in Legislative Language
One of the primary hurdles in implementing the nFADP is the occasionally vague language and ambiguous requirements within the legislation. Unlike the GDPR, which has been extensively discussed and interpreted, the nFADP is relatively new, and some aspects remain open to interpretation. This lack of clarity has necessitated seeking advice from Swiss data protection attorneys to comply with a nFADP.
Aligning Internal Policies
Aligning internal policies with the nFADP is challenging due to its less specific and more flexible standards than the GDPR. Companies must carefully interpret the appropriate measures for data transfers and handling third-party processors. This often involves detailed consultations and the development of compliance strategies to address the unique aspects of the nFADP.
Need for Legal Consultations
The vague requirements within the nFADP have prompted companies to engage with legal experts regularly. These consultations are essential to clarify the requirements and ensure that compliance strategies are robust and defensible. Legal consultations help bridge the gap between the legal text and practical implementation, ensuring businesses do not inadvertently breach the regulations.
Stakeholder Engagement
Effective implementation of the nFADP has required involving stakeholders early and often in the compliance process. This approach ensures all parties understand the new requirements and can provide insights into effective, user-centric data protection practices. Engaging stakeholders helps identify potential issues and develop practical solutions that align with legal requirements and business operations.
Iterative Refinements
Сompanies adopt dynamic compliance frameworks that allow for iterative refinements. This flexibility ensures compliance measures can be updated as new legal interpretations emerge or as technology evolves, maintaining adherence to the nFADP while optimizing data protection practices.
Technical Implementation Challenges
The technical implementation of the nFADP involves:
- Setting up systems for robust data security measures
- Adopting Privacy by Design and Default Principles
- Ensuring that technical and organizational measures (TOMs) are effective
This includes enhancing encryption protocols, implementing tiered access controls, and ensuring secure data storage and handling. Adapting infrastructure to meet these requirements often involves technical adjustments and an organizational cultural shift towards data security mindfulness.
Addressing Data Subject Rights
Implementing user interfaces that allow data subjects to easily exercise their rights under the nFADP, such as data portability, rectification, and erasure, has been a significant challenge. Companies have had to develop streamlined processes and interfaces to facilitate these rights, ensuring compliance while providing a user-friendly experience.
General Requirements of the New Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP)
The nFADP imposes several new obligations on businesses to ensure robust data protection practices. These nFADP’s requirements aim to enhance transparency, security, and the rights of data subjects. Below are the key general requirements businesses must adhere to under the nFADP.
Provide a Privacy Policy
Businesses must create and maintain a comprehensive privacy policy. Security policy should clearly outline the types of personal data collected, the purposes for data processing, and the rights of data subjects. It should be easily accessible to users, ensuring transparency in handling personal data.
Facilitate Data Subject Rights
Businesses are required to facilitate the rights of data subjects under the nFADP. These rights include access, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, data portability, and the right to object to data processing. Companies must implement mechanisms that allow data subjects to exercise these rights easily and effectively.
Ensure Adequate Data Security
Adequate data security measures must be in place to protect personal data against unauthorized access, loss, or destruction. This includes implementing technical and organizational measures (TOMs) such as encryption, access controls, and secure data storage. Businesses must regularly review and update these measures to ensure ongoing data security.
Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
For processing activities that pose a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals, businesses must conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs). DPIAs help identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them. This proactive approach ensures compliance and protects personal data.
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
While not mandatory, businesses are encouraged to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) or Data Protection Advisor (DPA). The DPO or DPA oversees data protection strategies and complying with the nFADP. This role includes providing advice on DPIAs, monitoring compliance, and acting as a point of contact for data subjects and regulatory authorities.
Implement Data Minimization Practices
Businesses must adhere to the principle of data minimization, which involves collecting only the personal data that is necessary for specific purposes. This reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures that data is not processed excessively. Implementing strict data minimization practices helps protect personal data and aligns with the core principles of the nFADP.
Regular Compliance Audits
Regular compliance audits are essential to ensure ongoing adherence to the nFADP. These audits should be conducted both internally and by third-party experts to identify and address any compliance gaps. Regular audits help reinforce data governance practices and ensure that data protection measures remain effective and up-to-date (IAPP) (Heydata).
Implementing nFADP Compliance: 10 Key Steps
1. Data Inventory and Mapping
To comply with a nFADP, businesses must conduct a comprehensive data inventory and mapping exercise. This involves identifying the organization’s personal data collected, processed, and stored.
2. Review and Update Privacy Policies
Businesses need to review and update their privacy policies to ensure they align with the nFADP requirements. The updated policies should provide:
- Clear and comprehensive information about the types of data collected
- The purpose of processing
- The rights of data subjects
3. Robust Consent Management Practices
This step involves designing mechanisms that allow users to give clear, affirmative consent for data processing activities. Users should also be able to withdraw their consent easily at any time. A key compliance requirement is ensuring that consent is informed and freely given.
4. Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Businesses must conduct DPIAs for any processing activities that present a high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms. DPIAs help identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them.
5. Implement Enhanced Data Security Measures
Businesses must implement advanced encryption techniques, establish strict access controls, and regularly review data storage practices. Ensuring data security is a fundamental requirement of the nFADP.
6. Facilitate Data Subject Rights
Organizations need to establish processes that allow data subjects to easily exercise their rights under the nFADP, such as the rights to access, rectification, erasure, and data portability.
7. Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) or Data Protection Advisor (DPA)
The DPO or DPA oversees data protection strategies, conducts audits, and serves as a point of contact for regulatory authorities and data subjects.
8. Regular Compliance Audits
Regular compliance audits, internally and through third-party experts, help identify gaps in compliance, assess the effectiveness of data protection measures, and ensure continuous improvement in data governance practices.
9. Training and Awareness Programs
These programs should educate staff about data protection principles, the importance of safeguarding personal data, and the specific requirements of the nFADP.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
This step involves keeping up-to-date with changes in data protection laws, technological advancements, and evolving best practices.
Django Stars Experience in Implementing nFADP Compliance
At DjangoStars, we have leveraged our extensive expertise in application development to help businesses achieve compliance with the Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP). Here’s a comprehensive look at our experience and the steps we took to implement nFADP compliance.
Project Planning and Approach
Our journey began with a thorough review of the official documentation available on the Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner’s website. This provided the foundational knowledge required to frame our compliance strategy.
We conducted extensive consultations, reviewed documentation, and participated in workshops with customers to clarify the nuances of the new law’s implementation. This collaborative approach ensured that every aspect of the nFADP was explored and understood.
Challenges in Interpretation and Implementation
Implementing the nFADP presented several challenges, primarily due to the occasionally vague language and ambiguous requirements within the legislation. To address this, we adopted a cautious approach, often planning for stricter compliance measures to ensure no breaches of regulatory requirements. Recognizing the nuanced differences between the GDPR and nFADP was crucial in our strategy. We integrated specific mandates tailored to the Swiss legal environment into our web application framework.
Addressing Implementation Challenges
Legal Consultations: Regular engagements with legal experts helped clarify vague requirements and ensured our compliance strategies were robust and defensible.
Stakeholder Engagement: Involving stakeholders early and often in compliance provided insights that shaped more effective and user-centric data protection practices.
Iterative Refinements: Our compliance framework is dynamic, allowing for iterative refinements based on evolving legal interpretations and technological advancements.
Implementation and Technical Details
Privacy Notice and Consent Management. We redesigned privacy notices to be more transparent and accessible, including detailed information about data collection, purposes of processing, and users’ rights. We also overhauled our consent mechanisms to allow users to make clear, affirmative choices about their data, which they could easily revise or withdraw.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). We implemented DPIA protocols for any new processing activity assessed as high risk. These assessments helped identify risks early in the development stages and apply mitigative strategies ingrained in the system’s architecture.
Data Minimization and Security Measures. Adhering to the principle of data minimization, we ensured that only essential data was collected. Our security measures were fortified by advanced encryption techniques and rigorous access controls, safeguarding data against unauthorized access and breaches.
Handling Data Subject Rights. We developed a streamlined interface within the application that allowed users to easily access their data and exercise their rights under the nFADP, such as data portability, rectification, and erasure.
Technical Enhancements
Enhanced Encryption Protocols. We introduced encryption measures for data at rest and in transit, ensuring that data is protected from unauthorized access throughout its lifecycle.
Robust Access Controls. A tiered access control system was implemented, where user permissions are strictly based on the principle of least privilege. Each user’s access is restricted to only the data and system functionalities necessary for their role, minimizing the potential for internal data breaches.
Secure Data Storage and Handling. We adopted encrypted databases and regularly reviewed our storage practices to align with nFADP requirements. This included the secure deletion of unnecessary or outdated data in compliance with the regulation’s demands for data minimization.
Procedural Enhancements
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs). DPIAs have become a routine part of our project lifecycle, especially when introducing new technologies or data processing methods that could impact user privacy. These assessments help identify risks early and shape the development process to mitigate potential data protection issues.
Regular Compliance Audits. To ensure ongoing compliance, we conduct regular audits both internally and by third-party experts. These audits help identify compliance gaps and reinforce our data governance practices.
Training and Awareness Programs. Recognizing that compliance is not solely a technical issue but also a human one, we significantly invested in training programs. These programs are designed to raise employees’ awareness of the importance of data protection and educate them on handling data responsibly.
Conclusion
The Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP) modernizes data privacy standards to align with the EU’s GDPR, enhancing data protection for individuals and businesses. Implementing nFADP compliance involves overcoming challenges related to legal ambiguities, requiring thorough legal consultations and stakeholder engagement.
Key steps for businesses include establishing privacy policies, facilitating data subject rights, and ensuring robust data security measures. Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) or advisor are good steps for proactive compliance. Regular compliance audits and comprehensive training programs are essential to maintain adherence and build a data protection culture.
Our approach to implementing nFADP compliance at DjangoStars reflects our deep respect for user privacy and our commitment to secure data handling practices. By integrating robust technical solutions with comprehensive procedural strategies, we are complying with the nFDAP regulations and enhancing our reputation as a trusted leader in technology and privacy at each stage of project development.
We look forward to assisting you in safeguarding your data and building trust with your users.
- Who does the nFADP apply to?
- The nFADP applies to all businesses and organizations operating in Switzerland that process personal data, regardless of the size or industry. This includes companies handling personal data of Swiss residents, even if the organization is based outside of Switzerland.
- What are the penalties for non-compliance with the nFADP?
- Non-compliance with the nFADP can result in severe penalties. Individuals responsible for intentional violations can face criminal sanctions up to CHF 250,000. Additionally, businesses may incur fines if they fail to identify the responsible person, leading to potential reputational damage and financial losses.
- How can DjangoStars help me implement nFADP compliance into my solution?
- DjangoStars offers comprehensive services to help businesses achieve nFADP compliance. Our team provides detailed assessments, legal consultations, and technical implementations, including data inventory and mapping, updating privacy policies, and ensuring robust data security measures.
- How to be compliant with the nFADP?
- To comply with the nFADP, conduct a thorough data inventory and update your privacy policies. Implement robust consent management, conduct DPIAs, enhance data security, facilitate data subject rights, appoint a DPO, and perform regular compliance audits.












