What Is Low-Code Development: A Complete Guide for Businesses in 2026

The global client wants one-click answers and is reluctant to wait, so businesses face increasing pressure to provide solutions faster. But how can one stay competitive and profitable if building a simple CRM may take forever?
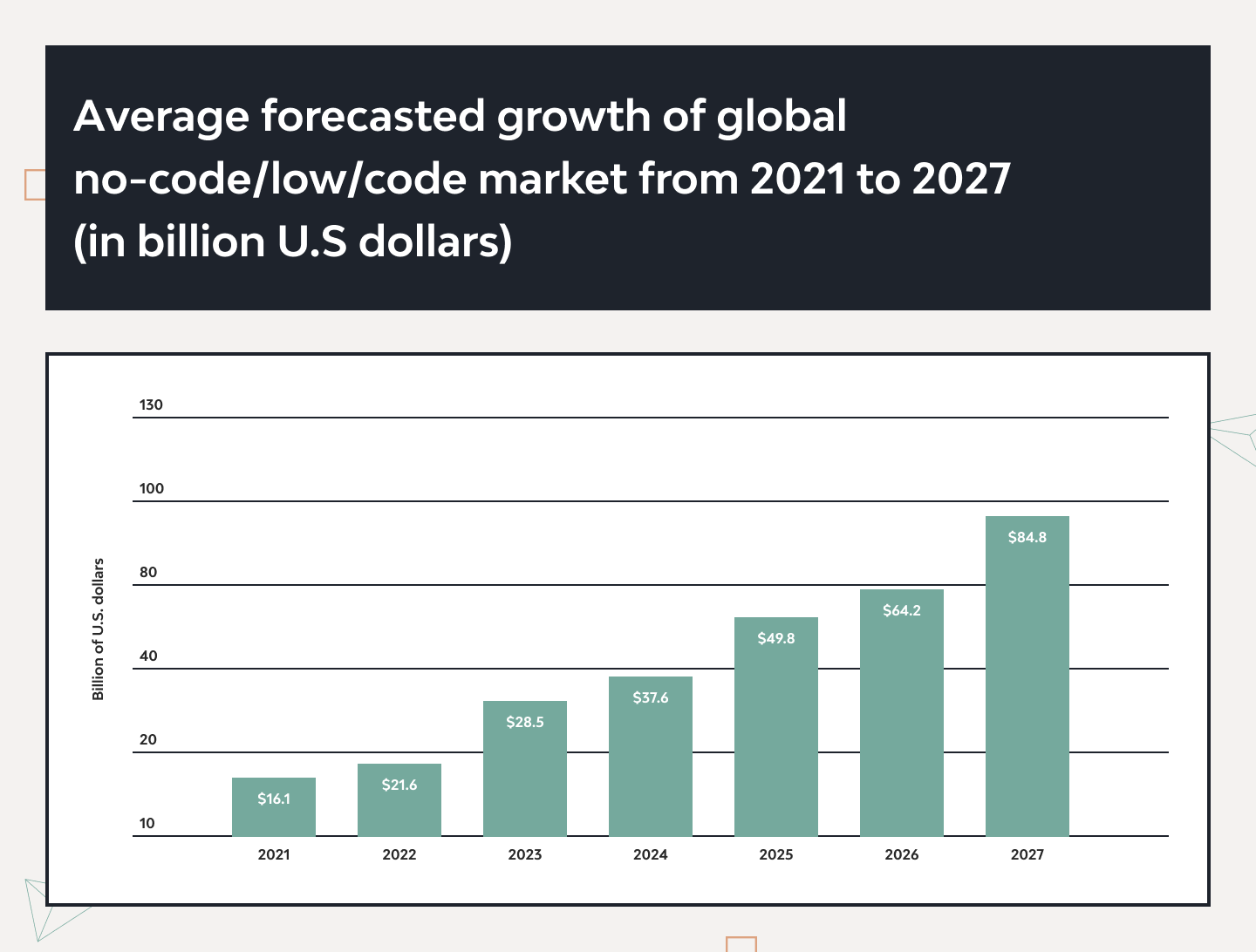
That’s when low-code development fills in the gap. Anyone with basic coding skills or enough curiosity to learn can make a simple app. The demand for low-code is huge and steadily growing: research shows that in two years, the global low-code/no-code market will reach $84.8 billion by 2027, which is a tremendous growth.
Low-Code Development: A Complete Guide for Businesses in 2026
But despite those advantages, low-code development is far from a one-size-fits-all solution. So, is it a good option for your company? Which benefits does it offer? And how do you know when low-code is the right choice and when it’s not? Find out from our comprehensive guide!
Low-code/no-code definition
Low-code is a development approach that allows businesses to build applications quickly and cost-effectively without extensive manual coding. Using various tools, you can create software as if you were playing with a building set.
However, unlike no-code, which is completely beginner-friendly yet much more limited in its capabilities, low-code still requires some programming knowledge. Here are some cases where this applies:
- Complex business logic. When an application needs advanced decision-making rules, numerous microservices, or intricate workflows, manual coding may be necessary.
- Advanced customization. If pre-built components don’t fully meet functionality requirements, developer input might be needed.
- Custom database queries or automation scripts. For optimized data retrieval or specific automated processes, SQL queries or scripting are required.
- API and third-party integrations. While many integrations are plug-and-play, some external services require custom coding.
If you want to try this technology, some of the most popular low-code platforms to explore may be Appian and Microsoft Power Apps for smaller projects or Mendix and OutSystems for enterprises. They are all known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, and broad integration capabilities.
Why use low-code application development?
Now, let’s dig deeper into why low code is important for businesses or startups and what makes this approach so popular.
- Accelerated software delivery. Visual interface, easy-to-use pre-built components, and robust integrations are an excellent base for speedy app development and fast deployment.
- Cost reduction opportunities. Low-code or no-code tools do not always require assistance from professional senior developers with high per-hour rates. The technology eliminates the need for large development teams or lengthy iterations.
- An open door for non-technical business users. Low-code development tools are designed to be used by the so-called citizen developers—people who can build and modify applications without extensive programming knowledge.
- Easier maintenance and updates. The same goes for software delivery; maintaining low-code apps also requires much less effort and costly developer time.
In a few words, making many kinds of apps using the low-code approach is much more time- and cost-efficient than traditional methods. These benefits of low-code are achieved through key low-code features that help the technology stand out and successfully compete with traditional coding, such as:
- Visual interface. Low-code platforms comprise pre-built components, templates, drag-and-drop functionality, and many more features that allow you to create the basis for the future app in almost no time compared to developing them from scratch.
- Automation tools. They enable businesses to create rule-based workflow automation or event triggers to handle tasks that would otherwise require manual intervention.
- Simplified third-party integrations. They provide pre-configured connectors and APIs that make it easy to integrate with payment gateways, CRMs, databases, cloud platforms, and other services. Now, imagine the time and effort saved due to reduced coding.
Though the low-code approach is popular overall, whether it is a good fit for your specific gap has to be determined. The answers vary from project to project, but certain benchmarks help cut through the noise of the doubt.
When is low-code development a right choice?
Here are the most typical cases where low-code is a good fit:
- If you need to launch an app quickly, low-code development platforms are your go-to option. As we mentioned previously, speed is one of the key advantages of this technology, so it can be great for startups: rapid prototyping or building an MVP can sometimes be easier with low-code tools.
- Budget constraints are another reason to consider low-code app development. Businesses needing non-complex applications, where extensive customization isn’t necessary, or internal tools like reporting dashboards can use low-code for reasonable pricing.
- For projects that require frequent updates or integration with existing systems, considering low-code is also a good idea. First, the technology allows for speedy iterations. And second, it opens the door for non-technical users who can now contribute.
In summary, you can potentially save time, significantly cut costs, and still get a quality app. In business language, it does sound like finding a Holy Grail, but is it always so?
When is low-code not applicable?
Low-code is a great option for modern development. However, there are some cases when it is not the best fit, and you would still require traditional coding.
- The flip side of low-code development simplicity is its limitations for projects with complex business logic or high customization requirements.
- With pre-built blocks, you can only get so far. However, for applications with intricate UX or in cases where the company needs complete control over design and functionality, traditional development is often a better choice.
- Low code is often a no-go for strict security and compliance demands. Here’s an example. One of our clients, the US-based B2B SaaS platform HowGood, needed to redesign its login flow to enhance security and usability. The platform is used by top global corporations like Danone and Nestlé; hence, security is a key priority. The technical solution we offered required deep expertise and traditional coding. While the creators of low-code technology provide a certain level of data protection, the risk of breaches with low-code or no-code is always higher than for custom-developed applications.
- Low-code platforms may struggle to support large-scale or performance-critical applications. If an internal dashboard crashes, it won’t take much time to fix, and there won’t be serious damage overall. However, for an Amazon-like e-commerce shop or a billing system, traditional coding is the only option.
- Long-term costs and vendor lock-in are additional risks to consider. While the benefits of low-code include lower initial investment and licensing fees, platform dependencies can add up over time. If a business needs to migrate from a low-code platform, transitioning to a fully custom solution can be costly and complex.
For better clarity, here’s a table that shows when low-code is a good fit and when it’s not:
| Type of application | Low-code? | Reasoning |
| Basic corporate website | Yes | Minimal customization, mostly static pages, low technical complexity. |
| Basic e-commerce store | Yes | Simple business logic, typical features, fast start of sales. |
| E-learning platform | Yes | Quick deployment, minimal coding for course management and content updates. |
| Internal CRM for SMEs | Yes | Fast setup, no compliance requirements, typical structure. |
| Customer support chatbots | Yes | Pre-built AI models, easy third-party integrations, automated processes. |
| HR management | Yes | HR processes are standardized and can be easily automated with low-code. |
| Internal business applications | Yes | Fast deployment, minimal development effort, citizen developers’ contribution. |
| MVPs and prototyping | Yes | Fast iterations, simple way to test the idea. |
| Workflow automation | Yes | Pre-built integrations and workflows simplify process automation. |
| Marketplace platform | No | Requires high customization, advanced workflows, and implies high load and flexible scalability. |
| Fintech app (e.g., payments, loans) | No | Strict compliance, security, and financial transaction reliability needed. |
| AI/ML-based application | No | Custom ML models require specialized frameworks and computational power. |
| SaaS product (B2B/B2C) | No | SaaS platforms need high scalability and flexibility. Some projects have strict compliance demands or industry regulations. |
| Healthcare management system | No | Sensitive personal data and strict regulatory compliance requirements. |
| Enterprise-scale system | No | Requires extensive customization, efficient performance, and long-term maintainability. |
| Highly customized solutions | No | Business logic complexity may exceed low-code capabilities. |
| Data-intensive applications | No | High data loads and real-time processing require scalability and reliability beyond low-code limitations. |
| Regulated industry applications | No | Full control over security, compliance, and governance is necessary. |
| Frequent third-party integrations | No | The level of complexity and custom API integrations demands manual coding and testing. |
| Performance-critical applications | No | Real-time performance, permanent availability, and infrastructure control are critical. |
While many types of apps can easily be built with low-code platforms, a wide range of those cannot.
Common Mistakes When Using Low-Code Platforms
In addition to cases when low-code may not be the best choice, human mistakes may eliminate many of the approach’s benefits. For example:
- Сhoosing the wrong low-code platform. Different solutions are not the same: some excel in automation, others in integrations, etc. Without a clear understanding of the goal and required features, there is a high chance of making a mistake.
- Security and compliance. Low-code development platforms typically do not come with top-notch data protection. Underestimating regulatory requirements may lead to paying twice when remaking your initial version.
- Attempting to build complex projects with low code. A lack of professional developer involvement can also backfire here, leading to limited functionality, weak security, poor architecture, and other issues.
- Lack of long-term planning. At first, low-code might seem like a fast solution to a lingering problem, but without projecting long-term growth, it can turn into a costly migration problem later on.
Now, let’s see where low-code development is evolving, which may be another point to consider before deciding whether it’s the right choice for you.
World-famous companies are already using these platforms to innovate faster, reduce costs, and scale efficiently.
Key Market Trends for Low-Code in 2026
First and foremost, like many technologies today, low-code development is becoming faster and more adaptable. Even though it’s not happening at lightning speed, AI-powered development assistants are set to streamline coding by offering suggestions, detecting errors, and even generating code snippets. But that’s not all:
- Advanced integrations and workflow optimization will allow businesses to connect their low-code applications seamlessly and accelerate innovation speed.
- Customization and flexibility will also improve with modular, composable applications. The technology will enable developers to reuse and reconfigure app components instead of building from scratch.
- As low-code security and compliance become more important, platforms will introduce stronger governance tools to meet regulatory standards.
- Finally, integrating low-code with traditional DevOps will bridge the gap between rapid application development and enterprise-grade deployment, allowing organizations to innovate quickly while maintaining control over their software lifecycle.
So, as we can see, the market is clearly moving toward a wider adoption of low-code solutions. Even though it won’t happen at once, many of the current challenges that make low-code unsuitable in some cases will be addressed in the future, which, in turn, means that:
- More companies won’t need massive dev teams to build solid apps and will turn to industry-specific low-code solutions.
- Marketing, HR, operations, and other business users are jumping in, using low-code to create tools according to their requirements. What is this, if not a digital transformation?
- Companies won’t just be building apps—they’ll combine low-code with AI, robotic process automation (RPA), and APIs to automate everything from customer service to supply chains.
- More businesses will use low-code to modernize legacy systems and streamline digital workflows.
It’s all about moving fast, cutting costs, and keeping up with the competition.
To Sum It Up
Low-code development is a simpler way for businesses to build software, offering speed, cost efficiency, and accessibility to non-technical users. With drag-and-drop interfaces, automation features, and easy integrations, companies can quickly develop applications while minimizing the need to deeply involve professional developers.
Low-code application platforms work best for rapid prototyping, internal tools, and business process automation. However, they may not be the best option for highly customized, security-sensitive, or performance-critical applications.
To choose between low-code and custom development, it’s always a good idea to start by evaluating your project’s complexity, security requirements, and long-term scalability.